How To Expand A Potentially Dangerous Shortened Url On Your Iphone
How to expand a potentially dangerous shortened URL on your iPhone is a crucial skill in today’s digital world. Shortened URLs, while convenient, can be used by scammers to trick you into clicking on malicious links. These links can lead to phishing scams, malware infections, and even identity theft.
It’s important to know how to identify these potentially dangerous links and how to safely expand them before clicking.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps of expanding a shortened URL on your iPhone using the Safari browser, along with some safety tips to help you stay protected. We’ll also discuss the importance of using reliable URL expander tools and services to ensure your safety.
Understanding Shortened URLs and Potential Dangers
Shortened URLs, also known as URL shorteners, are a common tool used to create shorter and more manageable links for sharing online. They’re especially helpful when dealing with long, complex URLs, making it easier to share links on social media, email, or instant messaging.
However, shortened URLs can also pose significant risks if you’re not careful.
Types of Shortened URLs
Shortened URLs come in various forms, with some of the most popular services including:
- bit.ly: This service is widely used for shortening URLs and tracking link clicks. It’s popular among businesses and individuals who want to analyze the effectiveness of their online campaigns.
- tinyurl: Another popular URL shortening service, tinyurl is known for its simplicity and ease of use. It allows users to create short URLs with a single click.
- rebrand.ly: This service focuses on creating branded short URLs, allowing users to customize their links with their own domain names. This can help enhance brand recognition and track specific campaigns more effectively.
Potential Risks Associated with Shortened URLs
While shortened URLs offer convenience, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks associated with clicking on them. Here are some of the most common dangers:
- Phishing Scams: Shortened URLs can be used to disguise malicious links, making it difficult to identify their true destination. Phishing scams often use shortened URLs to lure unsuspecting users into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Malware: Clicking on a shortened URL that leads to a malicious website can result in your device becoming infected with malware. This type of software can steal your personal data, track your online activity, or even damage your system.
- Privacy Concerns: Shortened URLs can be used to track your online activity and collect data about your browsing habits. Some services may share your information with third-party advertisers or other organizations, potentially compromising your privacy.
Identifying a Potentially Dangerous Shortened URL
You’ve learned about the potential dangers of shortened URLs. Now, it’s time to understand how to spot a potentially dangerous one. This knowledge can help you avoid falling victim to scams or malware.
Not all shortened URLs are malicious, but there are some red flags that can indicate a link might be dangerous. Let’s delve into those warning signs and learn how to analyze a shortened URL for legitimacy.
Red Flags Indicating a Dangerous Shortened URL
Recognizing these red flags can be a crucial first step in protecting yourself from malicious links.
- Unusual Domain Names:Shortened URLs often use generic or nonsensical domain names. For example, a shortened URL ending in “tinyurl.com” might not raise suspicion, but a URL like “qwe123.xyz” should. Be wary of URLs with unusual, short, or misspelled domain names.
- Suspicious Links:The actual destination of a shortened URL might not be clear. Look for links that seem out of place or that don’t match the context of the message. If you receive an unexpected email with a shortened URL to a website offering a free gift, it might be a phishing scam.
- Lack of Trust in the Source:If you receive a shortened URL from an unknown or untrusted source, exercise caution. Be wary of links sent through social media platforms, especially from unfamiliar accounts. Remember, even if the link comes from someone you know, it could have been compromised.
Examples of Phishing Scams Using Shortened URLs
Phishing scams often use shortened URLs to mask their true destination and lure unsuspecting victims into providing sensitive information. Here are some common examples:
- Fake Login Pages:You might receive an email claiming to be from a bank or other reputable institution, asking you to update your account information by clicking on a shortened URL. This link might redirect you to a fake login page designed to steal your credentials.
- Fake Promotions or Offers:You might see a social media post promoting a limited-time discount or free giveaway, but the link leads to a fake website that requests your personal information. This information can then be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes.
- Malware Downloads:A shortened URL could lead to a website that attempts to download malware onto your device. This malware can steal your data, monitor your online activity, or even take control of your device.
Assessing the Legitimacy of a Shortened URL, How to expand a potentially dangerous shortened URL on your iPhone
Here’s a guide to assessing the legitimacy of a shortened URL:
- Check the Source:Always consider the source of the shortened URL. If it comes from a trusted source, such as a known website or a reputable organization, you can feel more confident. However, if it comes from an unknown source or an unsolicited email, be cautious.
- Hover Over the Link:Most browsers allow you to hover over a link to see its destination before clicking. This can help you determine if the URL leads to a legitimate website or a suspicious one. If the destination URL seems suspicious, don’t click on the link.
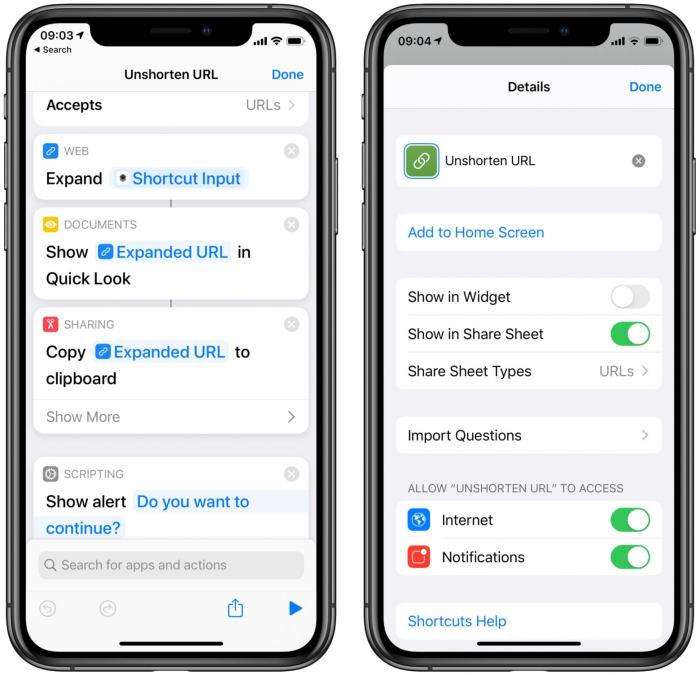
- Use a URL Expander:There are online tools and browser extensions that can expand shortened URLs to reveal their true destination. These tools can help you avoid clicking on malicious links.
- Trust Your Gut:If something about a shortened URL feels wrong, it probably is. If you’re unsure, don’t click on the link. It’s better to be safe than sorry.
Expanding a Shortened URL on iPhone
Knowing how to expand a shortened URL is essential for ensuring your online safety. By understanding the process, you can protect yourself from potential risks associated with malicious links.
Expanding a Shortened URL on iPhone Using Safari
This section explains how to expand a shortened URL on an iPhone using the Safari browser. Before expanding a shortened URL, it’s crucial to use a reliable URL expander tool or service. This ensures you are not redirected to a malicious website.
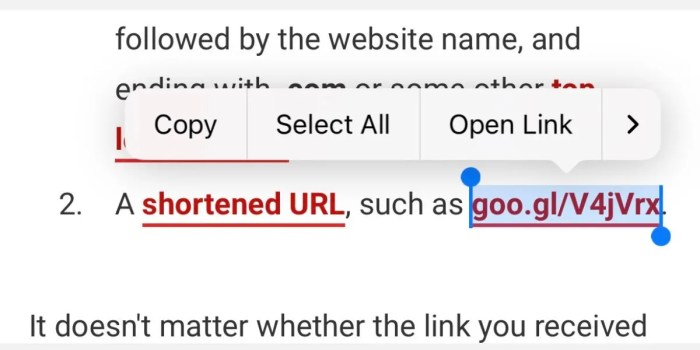
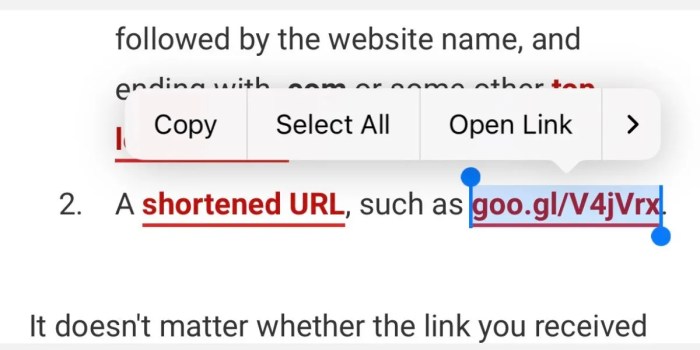
You know how sometimes you get a shortened URL that looks kinda sus? Well, on your iPhone, you can actually expand it to see where it’s really taking you. It’s super easy – just long-press the link and tap “Copy” to get the full URL.
Speaking of helpful iPhone tips, This Siri Shortcut will automatically text your commute time to your spouse – it’s a total lifesaver when you’re running late. Anyway, back to those shortened URLs – once you’ve copied the full version, you can paste it into your browser and check it out.
Better safe than sorry, right?
There are several reliable URL expander tools and services available online, such as:
- Google URL Shortener:This service is free and easy to use. It provides a simple interface for expanding shortened URLs.
- URL UnShortener:This website allows you to paste a shortened URL and view the expanded version. It also provides information about the URL, such as its destination and the website’s security rating.
- Bitly:This popular URL shortening service also offers a free URL expander tool. You can enter a shortened URL and view the expanded version, along with other information like the number of clicks the link has received.
To expand a shortened URL on your iPhone using the Safari browser, follow these steps:
- Open Safari and navigate to the shortened URL.
- Tap and hold the shortened URL.This will display a menu with various options.
- Select “Copy.”This will copy the shortened URL to your clipboard.
- Open a new tab in Safari.
- Paste the shortened URL into the address bar.You can do this by tapping and holding the address bar and selecting “Paste.”
- Press “Go.”This will navigate to the expanded version of the shortened URL.
After expanding the shortened URL, you can inspect the expanded version to determine if it’s legitimate. If the expanded URL looks suspicious or unfamiliar, do not proceed.Remember, it’s always best to exercise caution when clicking on shortened URLs. By using a reliable URL expander tool and following these steps, you can increase your online safety and protect yourself from potential risks.
Safety Measures for Expanding Shortened URLs: How To Expand A Potentially Dangerous Shortened URL On Your IPhone
Shortened URLs can be a convenient way to share links, but they can also be a way for malicious actors to spread malware or phishing scams. It’s important to be aware of the potential dangers and take steps to protect yourself.
Tips for Avoiding Suspicious Shortened URLs
It’s crucial to exercise caution when encountering shortened URLs. These tips can help you avoid clicking on links that could potentially harm your device:
- Hover over the link:Before clicking on a shortened URL, hover your mouse over it. Most browsers will display the actual destination URL in the bottom left corner of the browser window. If the destination URL looks suspicious, don’t click on the link.
You never know what you’re clicking on when you see a shortened URL, especially on your iPhone. If you’re ever unsure about a link, try pasting it into a URL expander or even just copying it into your browser’s address bar and hitting enter.
If you’re dealing with a forgotten password on your Mac, you can check out this guide on How to Reset Forgotten Passwords In OS X Lion. Once you’ve confirmed the link is safe, you can go ahead and click it!
- Check the sender:If you received the shortened URL in an email or text message, check the sender’s identity. If the sender is unknown or seems suspicious, don’t click on the link. You can use online tools like “Whois” to check the domain registration information for the sender’s website.
- Look for typos or grammatical errors:Phishing emails and malicious websites often contain typos or grammatical errors. If you see any errors in the shortened URL or the website it links to, be wary.
- Don’t click on links in unsolicited messages:Be cautious about clicking on links in emails or text messages from unknown senders, especially if they are asking you to provide personal information or download something.
- Use a URL scanner:There are many online URL scanners that can help you determine if a shortened URL is safe. These tools will analyze the destination URL and provide information about its safety.
Reporting Suspicious Links
If you encounter a shortened URL that you suspect is malicious, you can report it to the relevant authorities.
Ever get a shortened URL that makes you nervous? You can expand it on your iPhone by tapping the link, then tapping the little arrow that appears next to it. But before you click on anything, it’s always a good idea to check your location settings.
You can Stop following me! Tweak iPhone location settings to keep spies at bay. and make sure you’re not sharing more info than you want. Once you’re comfortable with your privacy settings, you can go back to expanding that URL and see where it takes you!
- Report to the website where you found the link:Many websites have reporting mechanisms for suspicious content. If you found the link on a social media platform, report it to the platform’s support team. You can also report the link to the website that shortened the URL, as they may be able to take action to remove it.
- Report to your internet service provider:Your internet service provider (ISP) may have a process for reporting suspicious websites or links.
- Report to the authorities:If you believe that a shortened URL is being used for criminal activity, you can report it to the authorities. In the United States, you can report it to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) or the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
Utilizing Security Software
Installing and using security software on your iPhone can provide an extra layer of protection against malicious websites and links.
- Antivirus software:Antivirus software can scan your iPhone for malware and protect you from malicious websites. There are many antivirus apps available for iPhone, such as McAfee Mobile Security, Norton Mobile Security, and Avast Mobile Security.
- Firewall:A firewall can help to prevent unauthorized access to your iPhone. iPhones have a built-in firewall, but you can also download third-party firewall apps.
- Privacy apps:Privacy apps can help to protect your personal information from being stolen. These apps can block trackers, prevent websites from accessing your location, and encrypt your data.
Best Practices for Sharing Links
Sharing links is a common practice in today’s digital world, but it’s important to do so safely and responsibly. Sharing shortened URLs can expose you to potential risks, so understanding the best practices for sharing links is crucial.
Sharing Original, Unshortened URLs
Whenever possible, it’s best to share the original, unshortened URL of a website or resource. This practice offers several advantages, including increased transparency and reduced risk of encountering malicious content. Sharing the original URL allows recipients to see the full address of the website, giving them a clearer picture of where they’re being directed.
This transparency helps users make informed decisions about whether to click on the link.
Using Trusted URL Shortening Services
While sharing original URLs is ideal, there are situations where using a URL shortener might be necessary, such as when sharing links on social media platforms with character limitations. If you choose to use a URL shortener, it’s essential to select a trusted service that prioritizes security and privacy.
Look for services that offer features like:
- Encryption:Ensures that the shortened URL and the destination URL are protected during transmission.
- Transparency:Provides a clear view of the original URL before clicking on the shortened link.
- Privacy Policies:Clearly Artikels how the service collects and uses user data.
Using Link Shorteners with Custom Branding and Analytics
Some URL shortening services offer advanced features that can enhance your link sharing experience. Custom branding allows you to personalize your shortened links with your own domain name or logo, adding a professional touch and building trust with recipients.
Analytics features provide insights into how your links are performing, including click-through rates and audience demographics. This data can be valuable for understanding the effectiveness of your link sharing campaigns and optimizing your strategies.
Last Recap
By learning how to expand shortened URLs and following our safety tips, you can navigate the digital world with greater confidence. Remember, always be cautious about clicking on shortened URLs, especially those from unfamiliar sources. Use your best judgment and never hesitate to report suspicious links to the appropriate authorities.
Stay safe out there, and happy browsing!
Quick FAQs
What if I accidentally click on a shortened URL?
If you accidentally click on a shortened URL, try to close the browser window immediately. You should also run a scan for malware on your device and change any passwords that may have been compromised. It’s also a good idea to contact your bank or credit card company to report any suspicious activity.
Are all shortened URLs dangerous?
No, not all shortened URLs are dangerous. Many legitimate websites use shortened URLs for convenience. However, it’s always best to be cautious and expand the URL before clicking on it.
How can I report a suspicious shortened URL?
You can report a suspicious shortened URL to the website or service that created it. You can also report it to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC) or the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).