Disable Integrated Graphics on Windows: When and How
How to Disable Integrated Graphics on Windows (and When You Should) sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american college casual language and brimming with originality from the outset.
Integrated graphics are a common feature on modern computers, but there are times when you may want to disable them. In this article, we’ll explain what integrated graphics are, why you might want to disable them, and how to do it on Windows.
Introduction
Integrated graphics are a common feature in modern computers. They are designed to provide basic graphics capabilities without the need for a dedicated graphics card. This can save money and space, and it can also reduce power consumption.
However, there are some potential benefits to disabling integrated graphics. For example, disabling integrated graphics can free up system resources, which can improve performance in some games and other applications. Additionally, disabling integrated graphics can reduce heat and power consumption, which can be beneficial for laptops and other portable devices.
When You Should Disable Integrated Graphics
- If you are experiencing performance issues in games or other applications, disabling integrated graphics may help to improve performance.
- If you are using a laptop or other portable device, disabling integrated graphics can help to reduce heat and power consumption.
- If you are using a dedicated graphics card, disabling integrated graphics can help to prevent conflicts between the two graphics cards.
Prerequisites
To successfully disable integrated graphics on Windows, you must ensure that your system meets certain hardware and software requirements.
The following are essential:
- A computer with a compatible motherboard
- A dedicated graphics card
- The latest version of Windows 10 or 11
Checking System Compatibility
Before proceeding, it’s crucial to verify that your system supports disabling integrated graphics.
- Open the Device Manager.
- Expand the “Display adapters” category.
- If you see two graphics cards listed, one of which is labeled “Intel HD Graphics” or “AMD Radeon Graphics,” your system supports disabling integrated graphics.
Methods for Disabling Integrated Graphics: How To Disable Integrated Graphics On Windows (and When You Should)
There are several methods for disabling integrated graphics in Windows. The choice of method depends on the specific hardware configuration and the operating system version. Here are some common methods:
Note:Before disabling integrated graphics, ensure that your computer has a dedicated graphics card installed and that it is properly connected and functioning.
Using Device Manager
Step 1:Open Device Manager by searching for it in the Windows search bar or by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Device Manager.”
Step 2:Expand the “Display adapters” category.
Step 3:Right-click on the integrated graphics adapter and select “Disable device.”
Step 4:Confirm the disabling by clicking “Yes” in the pop-up window.
Step 5:Restart your computer.
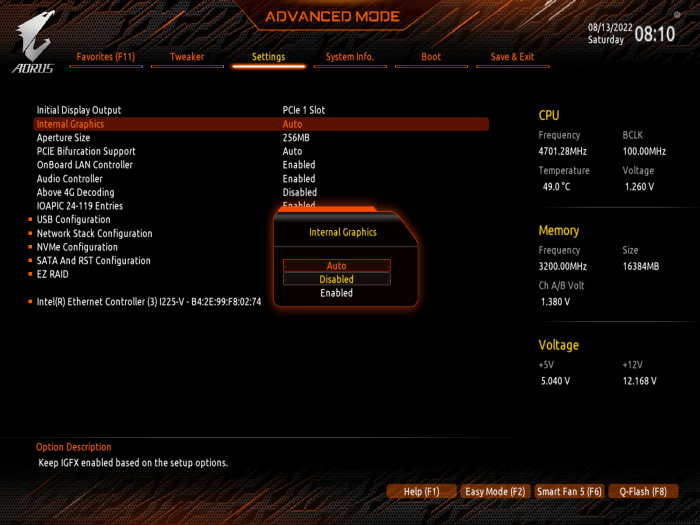
Using BIOS/UEFI Settings
Step 1:Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings. The key to enter BIOS/UEFI settings varies depending on the motherboard manufacturer. Common keys include F2, F10, F12, and Del.
Step 2:Navigate to the “Advanced” or “Peripherals” section in the BIOS/UEFI settings.
Step 3:Find the setting related to integrated graphics, which may be labeled as “Integrated Graphics,” “Onboard Graphics,” or “Primary Display Adapter.”
Step 4:Change the setting to “Disabled.”
Step 5:Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI settings.
Step 6:Restart your computer.
Using Registry Editor
Note:Editing the registry can be risky, so proceed with caution. It is recommended to create a backup of the registry before making any changes.
Step 1:Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2:Type “regedit” in the Run dialog box and click “OK” to open the Registry Editor.
Step 3:Navigate to the following registry key: “` HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GraphicsDrivers “`
Step 4:In the right pane, double-click on the “Configuration” DWORD value.
Step 5:Change the Value data to “0” to disable integrated graphics.
Step 6:Click “OK” to save the changes.
Step 7:Restart your computer.
BIOS Settings
Access the BIOS settings by pressing a specific key during system startup, usually F2, F10, or DEL. Consult your motherboard manual for the exact key.
Once in the BIOS, navigate to the “Advanced” or “Chipset” settings. Look for an option related to “Integrated Graphics” or “Graphics Configuration.”
Disable Integrated Graphics
- Locate the setting responsible for disabling integrated graphics, typically labeled as “Enable Integrated Graphics” or “IGPU Multi-Monitor.”
- Change the setting to “Disabled” or “Auto.”
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS. The system will automatically restart with integrated graphics disabled.
Device Manager
Device Manager allows you to disable integrated graphics in a few simple steps. It’s a powerful tool that gives you control over your hardware devices.
Steps to Disable Integrated Graphics Using Device Manager
- Press Windows Key+ Xand select Device Managerfrom the menu.
- Expand the Display Adapterscategory.
- Right-click on your integrated graphics device (usually labeled “Intel HD Graphics” or “AMD Radeon Graphics”) and select Disable Device.
- Confirm the disable operation by clicking Yesin the pop-up window.
Your integrated graphics will now be disabled. You can re-enable it by following the same steps and selecting Enable Deviceinstead.
Registry Editor
The Registry Editor is a powerful tool that allows you to modify the settings of your Windows operating system. However, it’s important to use caution when making changes to the registry, as incorrect modifications can cause your system to become unstable or even crash.
To disable integrated graphics using the Registry Editor, follow these steps:
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type “regedit” into the Run dialog box and press Enter.
- Navigate to the following registry key:
- In the right-hand pane, double-click on the “Configuration” value.
- In the “Value data” field, change the value to “0” and click OK.
- Restart your computer.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GraphicsDrivers
Warnings
It’s important to note that disabling integrated graphics can have some negative consequences. For example, you may experience a decrease in performance when playing games or running other graphics-intensive applications. Additionally, some laptops and other devices may not function properly without integrated graphics.
If you’re not sure whether or not you should disable integrated graphics, it’s best to consult with a qualified computer technician.
Dedicated Graphics Card
A dedicated graphics card is a separate hardware component installed in a computer system, specifically designed to handle graphics processing tasks. It plays a crucial role in disabling integrated graphics by providing superior graphics capabilities, allowing the system to allocate resources more efficiently.
Using a dedicated graphics card offers several benefits. It enhances gaming performance by delivering smoother gameplay, higher frame rates, and improved visual quality. Additionally, it accelerates video editing and rendering processes, enabling faster completion of creative projects. Dedicated graphics cards also provide support for advanced graphics technologies such as ray tracing and DLSS, offering realistic and immersive experiences.
Drawbacks, How to Disable Integrated Graphics on Windows (and When You Should)
However, there are also some drawbacks to using a dedicated graphics card. They can be more expensive than integrated graphics, adding to the overall cost of the system. Additionally, dedicated graphics cards consume more power, leading to increased energy consumption and potentially higher electricity bills.
They also require more space within the computer case, which may be a limitation for compact builds.
When to Disable Integrated Graphics
Disabling integrated graphics may be advisable in certain situations.When using a dedicated graphics card, disabling integrated graphics can improve performance and reduce system resource usage. Integrated graphics share system memory with the CPU, potentially limiting the performance of both components.
Disabling integrated graphics allows the dedicated graphics card to utilize all available system memory, resulting in smoother gameplay, faster rendering, and improved overall performance.Additionally, disabling integrated graphics can be beneficial when troubleshooting hardware issues. If you encounter display problems or system instability, disabling integrated graphics can help isolate the issue to the dedicated graphics card or other system components.
By eliminating the integrated graphics as a potential source of the problem, you can narrow down the troubleshooting process and identify the root cause more efficiently.
Potential Issues
Disabling integrated graphics can potentially lead to certain issues that require attention. Here’s an overview of some common problems and troubleshooting tips to help resolve them:
One potential issue is the inability to display visuals on the screen. This can occur if the dedicated graphics card is not properly installed or configured. Ensure that the graphics card is securely seated in the PCIe slot and that the necessary drivers are installed.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Verify that the dedicated graphics card is properly seated in the PCIe slot and secured with the screws.
- Update the drivers for the dedicated graphics card to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- If the issue persists, try using a different PCIe slot or reseating the graphics card to eliminate any potential hardware issues.
Re-enabling Integrated Graphics
If you later decide you want to use integrated graphics again, you can easily re-enable it.
The method for re-enabling integrated graphics varies depending on the method you used to disable it.
BIOS Settings
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS settings.
- Locate the graphics settings and change the primary graphics device back to the integrated graphics card.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
Device Manager
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand the Display adapters section.
- Right-click on the dedicated graphics card and select Disable device.
- Restart your computer.
Registry Editor
- Open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GraphicsDrivers.
- Locate the Configuration value and change the value data to 0.
- Restart your computer.
Final Wrap-Up
Disabling integrated graphics can be a useful way to improve performance or troubleshoot problems. However, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons before making a decision. If you’re not sure whether or not you should disable integrated graphics, consult with a qualified technician.
FAQ
What are integrated graphics?
Integrated graphics are a type of graphics processing unit (GPU) that is built into the motherboard of a computer. They are less powerful than dedicated graphics cards, but they are more affordable and consume less power.
Why would I want to disable integrated graphics?
There are several reasons why you might want to disable integrated graphics. For example, you may want to:
- Improve performance in games or other graphics-intensive applications.
- Troubleshoot problems with your computer’s display.
- Use a dedicated graphics card.
How do I disable integrated graphics on Windows?
There are several ways to disable integrated graphics on Windows. The most common method is to use the BIOS settings. You can also use the Device Manager or the Registry Editor.