Guide To Overclocking Your Cpu Safely
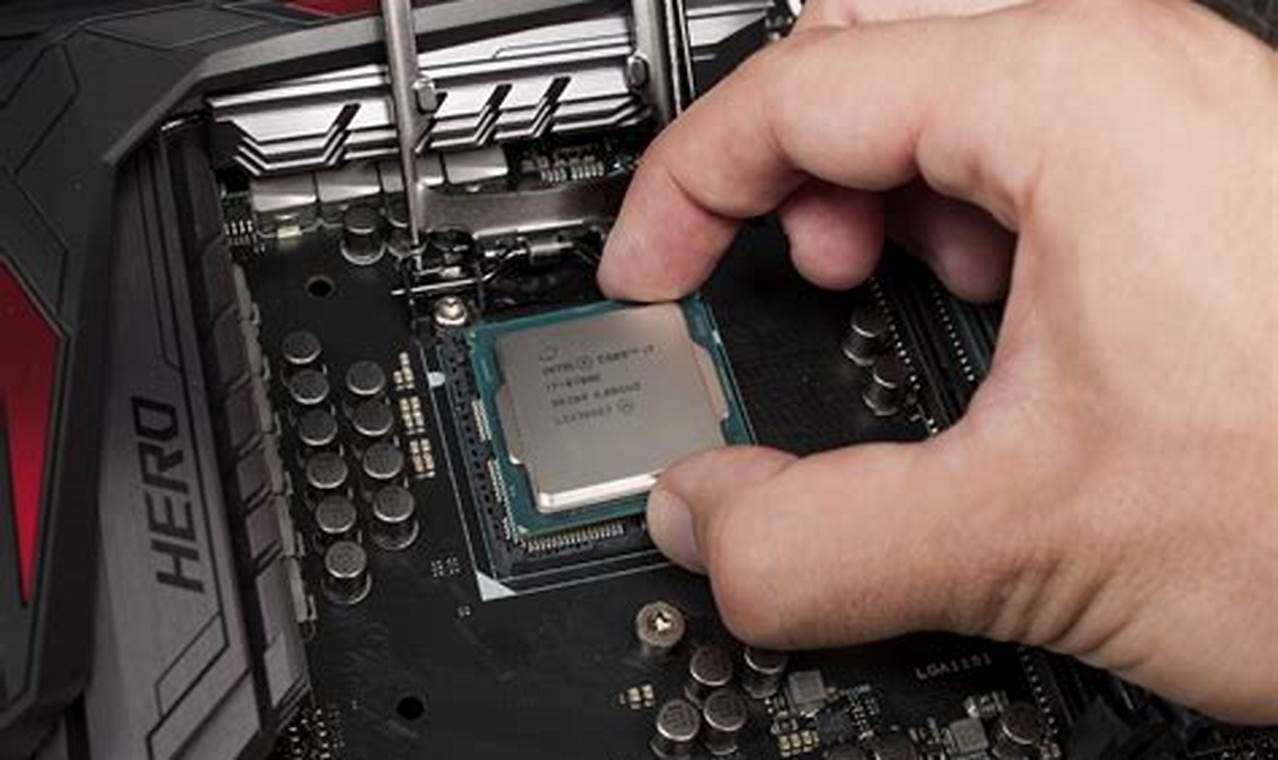
A guide to overclocking your CPU safely is a set of instructions that teach you how to increase the clock speed of your CPU without damaging it. Overclocking can improve the performance of your computer, but it is important to do it safely to avoid damaging your hardware.
Overclocking can be beneficial for gamers, video editors, and other users who need the extra performance. However, it is important to note that overclocking can also void your CPU’s warranty. The first overclocking was done in 1977 by Jerry Sanders, the co-founder of AMD. Sanders overclocked an Intel 8080A microprocessor from 2 MHz to 4 MHz, doubling its speed.
This article will discuss the basics of overclocking, including the different methods, the risks involved, and how to do it safely. We will also provide some tips on how to get the most out of your overclocked CPU.
Guide to Overclocking Your CPU Safely
Overclocking your CPU can be a great way to improve its performance, but it is important to do so safely. There are a number of key aspects to consider when overclocking your CPU, including:
- Voltage: The voltage supplied to your CPU is one of the most important factors to consider when overclocking. Increasing the voltage can help your CPU to reach higher clock speeds, but it can also damage your CPU if it is not done carefully.
- Temperature: The temperature of your CPU is another important factor to consider when overclocking. Overclocking can cause your CPU to run hotter, so it is important to ensure that your cooling system is adequate.
- Stability: It is important to ensure that your overclock is stable before using your computer for everyday tasks. An unstable overclock can cause your computer to crash or freeze.
- Monitoring: It is important to monitor your CPU’s voltage, temperature, and stability when overclocking. This will help you to identify any potential problems and prevent damage to your CPU.
- Research: It is important to do your research before overclocking your CPU. There are a number of resources available online that can help you to learn more about overclocking and how to do it safely.
- Patience: Overclocking can be a time-consuming process. It is important to be patient and to take your time when overclocking your CPU.
- Experience: Overclocking is a skill that takes time and practice to develop. If you are new to overclocking, it is best to start with a small overclock and gradually increase the clock speed as you gain experience.
- Hardware: The type of hardware you have will also affect your ability to overclock your CPU. Some motherboards and CPUs are better suited for overclocking than others.
These are just a few of the key aspects to consider when overclocking your CPU. By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your overclock is safe and successful.
Voltage
Voltage is a critical component of overclocking because it affects the stability and performance of your CPU. Increasing the voltage can allow your CPU to reach higher clock speeds, but it can also increase the temperature of your CPU and shorten its lifespan. Therefore, it is important to find a balance between voltage and clock speed to ensure that your CPU is stable and performs well without being damaged.
A good way to start overclocking is to increase the voltage by small increments and test the stability of your system. If your system is stable, you can continue to increase the voltage until you reach the desired clock speed. However, if your system becomes unstable, you should decrease the voltage until it is stable again.
It is also important to monitor the temperature of your CPU when overclocking. If the temperature of your CPU becomes too high, it can damage your CPU. Therefore, you should use a cooling system that is adequate for your overclocked CPU.
By following these tips, you can safely overclock your CPU and improve its performance.
Temperature
Temperature is a critical component of overclocking because it affects the stability and performance of your CPU. When you overclock your CPU, you are increasing the voltage and clock speed of your CPU. This can cause your CPU to run hotter than normal. If your cooling system is not adequate, your CPU may overheat and become unstable.
There are a number of ways to ensure that your cooling system is adequate for overclocking. You can use a larger heatsink, a more powerful fan, or a liquid cooling system. It is also important to make sure that your case has good airflow.
If you are not sure whether your cooling system is adequate for overclocking, it is best to err on the side of caution and use a more powerful cooling system. Overheating your CPU can damage your CPU, so it is important to make sure that your cooling system is up to the task.
Here are some real-life examples of how temperature can affect overclocking:
- If you overclock your CPU too much, it may overheat and cause your computer to crash.
- If your cooling system is not adequate, your CPU may overheat and throttle its performance.
- If you use a liquid cooling system, you may be able to overclock your CPU more than you would be able to with a traditional air cooler.
By understanding the relationship between temperature and overclocking, you can safely overclock your CPU and improve its performance.
Stability
Stability is an important aspect of overclocking because it ensures that your system will run reliably without crashing or freezing. If your overclock is unstable, it may cause your computer to crash during gaming, video editing, or other demanding tasks. It can also cause your computer to freeze, which can lead to data loss.
-
Testing Stability
The best way to test the stability of your overclock is to run a stress test. A stress test is a software program that puts your CPU under a heavy load for an extended period of time. If your computer crashes or freezes during a stress test, it means that your overclock is unstable and you need to reduce the clock speed or voltage until it is stable.
-
Monitoring Temperatures
Another important aspect of stability is monitoring your CPU’s temperature. When you overclock your CPU, it will run hotter than normal. If the temperature of your CPU gets too high, it can cause your computer to crash or freeze. Therefore, it is important to use a good cooling system and to monitor your CPU’s temperature when overclocking.
-
Using Quality Components
The quality of your components can also affect the stability of your overclock. If you are using low-quality components, they may not be able to handle the increased stress of overclocking. Therefore, it is important to use high-quality components when overclocking your CPU.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your overclock is stable and reliable.
Monitoring
Monitoring your CPU’s voltage, temperature, and stability is a critical component of overclocking safely. By monitoring these factors, you can identify any potential problems and prevent damage to your CPU.
For example, if you overclock your CPU too much, you may notice that the voltage is too high, the temperature is too high, or the system is unstable. By monitoring these factors, you can identify the problem and take steps to correct it.
Monitoring your CPU’s voltage, temperature, and stability is also important for long-term reliability. Over time, overclocking can degrade your CPU if it is not properly monitored. By monitoring these factors, you can ensure that your CPU is operating within safe limits and extend its lifespan.
There are a number of software tools that you can use to monitor your CPU’s voltage, temperature, and stability. Some popular tools include:
- HWMonitor
- Core Temp
- RealTemp
- AIDA64
Once you have installed a monitoring tool, you can use it to monitor your CPU’s voltage, temperature, and stability while overclocking. This will help you to identify any potential problems and prevent damage to your CPU.
Research
Research is a crucial part of overclocking your CPU safely. By doing your research, you can learn about the different aspects of overclocking, the risks involved, and how to do it safely. There are a number of resources available online that can help you to learn more about overclocking, including articles, tutorials, and videos.
-
Understanding the Basics
The first step to overclocking your CPU safely is to understand the basics of overclocking. This includes learning about the different components involved in overclocking, the different types of overclocking, and the risks involved.
-
Finding the Right Resources
Once you have a basic understanding of overclocking, it is important to find the right resources to help you learn more. There are a number of websites, forums, and videos that can provide you with valuable information about overclocking.
-
Learning from Others
One of the best ways to learn about overclocking is to learn from others. There are a number of online communities where you can connect with other overclockers and share your experiences.
-
Testing and Experimenting
Once you have learned the basics of overclocking and found the right resources, it is time to start testing and experimenting. This is the best way to learn what works and what doesn’t.
By following these tips, you can do your research and learn how to overclock your CPU safely. Remember, overclocking is a complex process, so it is important to take your time and do your research before you start.
Patience
Overclocking your CPU can be a time-consuming process, but it is important to be patient and to take your time. Rushing the process can lead to mistakes that can damage your CPU.
One of the most important things to remember when overclocking is that every CPU is different. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to overclocking. What works for one CPU may not work for another.
It is important to start with small overclocks and gradually increase the clock speed and voltage until you reach the desired performance. Monitoring your CPU’s temperature and stability is also important to ensure that you are not pushing your CPU too hard.
If you are not patient when overclocking, you may end up damaging your CPU. By taking your time and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can safely overclock your CPU and improve its performance.
Experience
Experience is a crucial aspect of overclocking safely and effectively. Overclocking requires a deep understanding of your hardware, as well as the ability to identify and troubleshoot potential problems. Without experience, it is easy to make mistakes that can damage your CPU or other components.
-
Starting Small:
When you are first starting out, it is important to start with small overclocks and gradually increase the clock speed as you gain experience. This will help you to identify and troubleshoot any potential problems before they cause damage to your CPU.
-
Testing and Monitoring:
It is also important to test your overclocks thoroughly and monitor your system’s stability. This will help you to ensure that your overclock is stable and will not cause any problems.
-
Research and Learning:
Overclocking is a complex process, and there is always more to learn. By reading articles, watching videos, and talking to other overclockers, you can learn more about the process and how to do it safely.
-
Patience and Practice:
Overclocking is not something that you can master overnight. It takes time and practice to develop the skills and knowledge necessary to overclock safely and effectively.
By following these tips, you can gain the experience necessary to overclock your CPU safely and effectively. Remember, overclocking is a journey, not a destination. The more you learn and practice, the better you will become at it.
Hardware
The type of hardware you have will also affect your ability to overclock your CPU. Some motherboards and CPUs are better suited for overclocking than others. For example, motherboards with better power delivery and cooling will be able to handle higher overclocks. CPUs with more cores and threads will also be able to handle higher overclocks.
-
Motherboard:
The motherboard is a critical component for overclocking. It provides the power and cooling for the CPU, and it also determines the maximum overclocking potential of the CPU.
-
CPU:
The CPU is the other critical component for overclocking. The number of cores and threads, as well as the base clock speed, will all affect the overclocking potential of the CPU.
-
RAM:
The RAM can also affect the overclocking potential of the CPU. Faster RAM can help to reduce latency and improve performance.
-
Cooling:
The cooling system is also important for overclocking. A better cooling system will allow you to reach higher overclocks without damaging the CPU.
By understanding the different hardware components that can affect overclocking, you can make informed decisions about which components to upgrade in order to improve your overclocking potential.
FAQs
This FAQ section addresses common questions and concerns related to overclocking your CPU safely. It provides concise answers to help you understand the process and avoid potential pitfalls.
Question 1: What is the primary benefit of overclocking my CPU?
Overclocking can enhance your CPU’s performance, resulting in faster processing speeds and improved gaming or application responsiveness.
Question 2: Is overclocking safe for my CPU?
Overclocking can be safe if done carefully. By following proper guidelines and monitoring your system, you can minimize risks to your CPU.
Question 3: How do I know if my overclock is stable?
To ensure stability, run stress tests and monitor your system’s temperature and performance. If your system remains stable under load, your overclock is likely safe.
Question 4: What are the potential risks of overclocking?
Excessive overclocking can lead to system instability, reduced lifespan of your CPU, or even permanent damage if not done properly.
Question 5: How much should I overclock my CPU?
The optimal overclocking level depends on your specific CPU and cooling system. Start with small increments, monitor your system, and gradually increase the overclock until you reach a balance between performance and stability.
Question 6: What tools can I use to monitor my CPU while overclocking?
Various software tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, and AIDA64 allow you to monitor your CPU’s temperature, voltage, and other vital parameters during overclocking.
In summary, overclocking your CPU can enhance its performance, but it’s crucial to approach it with caution and a thorough understanding of the process to ensure safety and avoid potential risks.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the technical aspects of overclocking and provide detailed guidance on how to overclock your CPU safely and effectively.
Tips to Overclock Your CPU Safely
This section provides practical and actionable tips to overclock your CPU safely, maximizing performance while minimizing risks. Follow these guidelines to optimize your overclocking experience.
Tip 1: Start Gradually: Begin with small overclocks and incrementally increase the settings. This allows you to monitor stability and prevent excessive voltage or heat.
Tip 2: Monitor Temperatures: Use software to monitor CPU temperature during overclocking. Ensure it stays within safe limits to avoid thermal damage.
Tip 3: Prioritize Stability: Stress test your overclock to assess its stability. Run demanding applications or use specialized software to detect any potential issues.
Tip 4: Optimize Cooling: Invest in a high-quality CPU cooler, such as an air cooler or liquid cooling system. Efficient cooling is essential for maintaining stability at higher clock speeds.
Tip 5: Understand Your BIOS: Familiarize yourself with your motherboard’s BIOS settings. Learn how to adjust voltage, multipliers, and other parameters to achieve optimal overclocking.
Tip 6: Research Your Hardware: Different CPUs and motherboards have varying overclocking capabilities. Research your specific components to determine their safe limits and potential for overclocking.
Tip 7: Seek Expert Advice: Consult reputable forums or overclocking communities to learn from experienced overclockers. They can provide valuable insights and guidance tailored to your specific hardware.
By following these tips, you can increase your chances of overclocking your CPU safely and effectively. Remember, overclocking is an iterative process that requires patience, monitoring, and a deep understanding of your hardware.
In the concluding section, we will provide a comprehensive summary of the key aspects of overclocking and emphasize the importance of safety and responsible practices.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the intricacies of overclocking your CPU safely and effectively, emphasizing the importance of understanding your hardware, monitoring system parameters, and proceeding with caution. Overclocking can unlock significant performance gains, but it is crucial to approach it responsibly to avoid potential risks.
Key insights from this article include:
- Overclocking involves increasing the clock speed of your CPU to enhance its performance, but it must be done judiciously to ensure stability and longevity.
- Monitoring CPU temperature, voltage, and stability is paramount throughout the overclocking process to identify and address any issues promptly.
- Understanding the specific capabilities and limitations of your CPU and motherboard is essential for successful and safe overclocking.
Remember, overclocking is a journey that requires patience, research, and a commitment to safety. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can harness the performance benefits of overclocking while safeguarding your hardware investment. Embrace the challenge, learn from experienced overclockers, and enjoy the rewards of a well-tuned system.