Adobe Flash Player Is Dead Here’S How To Remove It From Your Mac.
Adobe Flash Player is dead Here’s how to remove it from your Mac. – Adobe Flash Player is dead. Here’s how to remove it from your Mac. Remember those days when Flash Player was the king of the web, powering everything from online games to interactive websites? It’s hard to believe that Flash Player is now a relic of the past, but its time has come to an end.
As technology evolved, security concerns arose, and HTML5 emerged as a superior alternative, Flash Player’s reign was brought to a close.
But don’t worry, removing Flash Player from your Mac is a simple process. We’ll guide you through the steps, ensuring that your Mac is free from this outdated technology.
The End of an Era
Remember those days when websites were filled with interactive animations, engaging games, and captivating video content? The mastermind behind this digital magic was Adobe Flash Player, a technology that revolutionized the internet landscape for over two decades.
The Rise and Reign of Flash Player
Adobe Flash Player, originally known as FutureSplash Animator, emerged in 1996 as a revolutionary tool for creating dynamic and interactive web content. Its ability to deliver high-quality animations, streaming video, and engaging games made it a game-changer in the early days of the internet.
Flash Player quickly gained popularity, becoming the standard for web developers and users alike.
- Interactive Web Experiences:Flash Player enabled websites to go beyond static pages, offering interactive elements like games, quizzes, and animated banners. This interactivity brought a new level of engagement to online experiences.
- Streaming Video and Audio:Flash Player was instrumental in the early days of online video streaming. It allowed users to watch videos directly on their web browsers, paving the way for platforms like YouTube and Vimeo.
- Rich Media Content:Flash Player provided a platform for delivering rich media content, including complex animations, 3D graphics, and interactive games. This capability opened up new possibilities for creative expression and entertainment on the web.
Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Adobe Flash Player was a popular technology for interactive web content, but its widespread use also made it a prime target for hackers and malware. Flash Player’s complex architecture and reliance on outdated security models made it vulnerable to various exploits, posing significant security risks to users.
Vulnerabilities and Exploits
Flash Player’s vulnerabilities made it a target for hackers seeking to exploit these weaknesses for malicious purposes. These vulnerabilities often stemmed from:
- Memory Corruption:Flash Player’s memory management was prone to errors, allowing attackers to overwrite memory locations and execute arbitrary code.
- Sandbox Escapes:The sandbox, designed to isolate Flash content from the user’s system, could be bypassed by attackers, enabling them to access sensitive data or install malware.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):Attackers could inject malicious JavaScript code into Flash content, which could then be executed by unsuspecting users, potentially stealing credentials or installing malware.
These vulnerabilities led to numerous exploits and attacks, some of which had significant consequences. For example, in 2010, a critical vulnerability in Flash Player allowed attackers to remotely execute code on vulnerable systems, potentially installing malware or stealing sensitive information.
This vulnerability was exploited in the “Operation Aurora” attack, which targeted Google and other tech companies.
Examples of Past Exploits and Attacks
- “Operation Aurora” (2010):This attack, attributed to a Chinese government-linked hacking group, exploited a Flash Player vulnerability to steal intellectual property from Google and other tech companies.
- “Stuxnet” (2010):This sophisticated malware, believed to be developed by the US and Israel, targeted Iranian nuclear facilities. While not directly targeting Flash Player, it exploited a vulnerability in Windows operating systems, which could have been used in conjunction with a Flash Player vulnerability.
- “Blackhole Exploit Kit” (2011-2013):This notorious exploit kit used Flash Player vulnerabilities to deliver malware to unsuspecting users. It was responsible for numerous infections, including ransomware and banking trojans.
These examples highlight the severity of security risks associated with Flash Player and the need for its eventual deprecation.
The Transition to HTML5
The demise of Flash Player paved the way for HTML5, a robust web technology that revolutionized web development and content delivery. HTML5, the latest version of the language that defines the structure and content of web pages, emerged as a powerful alternative to Flash Player, offering a more versatile and secure approach to web content creation.HTML5’s rise can be attributed to its ability to handle multimedia, interactive elements, and advanced graphical features without relying on external plugins.
This eliminates the need for users to install Flash Player, streamlining the web browsing experience and reducing security risks.
Comparison of Flash Player and HTML5
HTML5 and Flash Player offer distinct capabilities. Flash Player, initially popular for its rich multimedia features and animation capabilities, faced limitations in areas like cross-platform compatibility and security. HTML5, on the other hand, provides a standardized approach to web development, enabling developers to create dynamic and interactive content across various platforms and devices.
- Multimedia Support: HTML5 provides built-in support for audio and video playback, eliminating the need for external plugins. Flash Player, while initially popular for multimedia content, required users to install the plugin, leading to compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities.
- Interactivity: HTML5 offers a range of features for creating interactive web applications, including canvas for drawing graphics, geolocation for location-based services, and WebSockets for real-time communication. Flash Player also provided interactive capabilities, but HTML5’s standardized approach ensures wider compatibility and easier development.
- Security: HTML5 prioritizes security, integrating features like content security policy (CSP) and sandboxing to mitigate vulnerabilities. Flash Player’s security flaws, which were often exploited by malicious actors, led to widespread security concerns.
Benefits of HTML5
The transition to HTML5 has brought several advantages to the web ecosystem. Its open standards, security enhancements, and improved performance have made it the preferred choice for web developers and content creators.
- Enhanced Security: HTML5’s security features, such as CSP and sandboxing, significantly reduce the risk of vulnerabilities and malicious attacks. This makes the web browsing experience safer for users.
- Improved Performance: HTML5 is optimized for performance, enabling faster loading times and smoother user interactions. Flash Player’s reliance on plugins often resulted in slower performance and resource consumption.
- Accessibility: HTML5 adheres to accessibility standards, making web content accessible to users with disabilities. Flash Player’s accessibility features were limited, hindering inclusivity.
Removing Flash Player from Mac
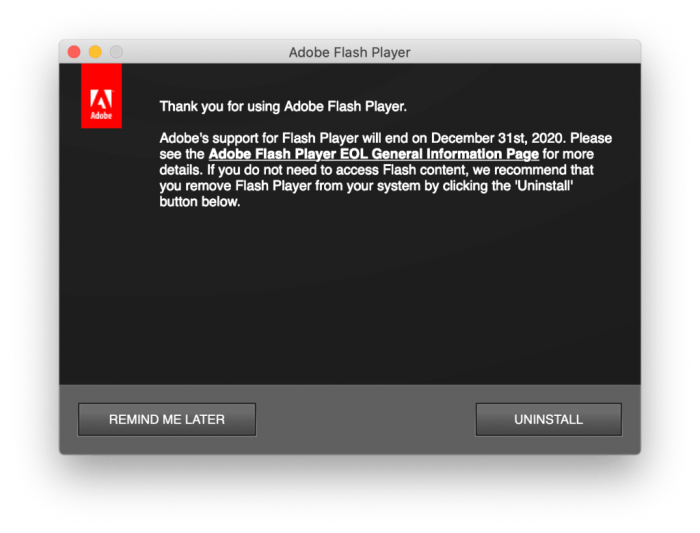
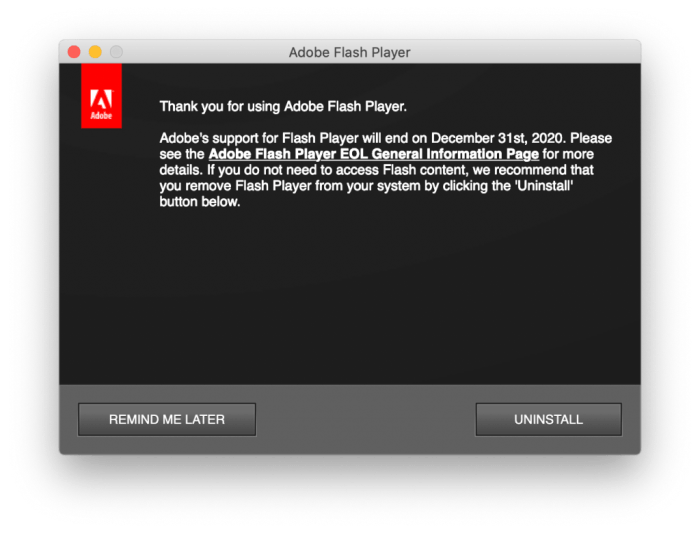
Now that Flash Player is officially dead, it’s time to remove it from your Mac to ensure security and a smooth browsing experience. This process is straightforward and can be done in a few simple steps.
Removing Flash Player Using the Adobe Website
Adobe provides a dedicated tool for uninstalling Flash Player from your Mac. This method is the most reliable and ensures a clean removal.
- Visit the Adobe Flash Player uninstall page at https://helpx.adobe.com/flash-player/kb/uninstall-flash-player-mac.html .
- Click the “Uninstall” button to download the Flash Player uninstaller.
- Open the downloaded file and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation process.
Using Third-Party Uninstaller Tools
While not strictly necessary, using a third-party uninstaller tool can be helpful for removing Flash Player completely and ensuring no leftover files remain.
So, you’re finally ditching that dusty old Adobe Flash Player? Good riddance! While you’re cleaning up your digital space, you might want to check out How to stop your Photos library from taking over your Mac. It’s a great way to free up some precious storage space, especially if you’re a photography enthusiast.
Once you’ve cleared out those unnecessary files, you’ll have plenty of room for all your new apps, and who knows, maybe even some fun new games that don’t require Flash!
- Some popular uninstaller tools include AppCleaner, CleanMyMac X, and Revo Uninstaller.
- These tools scan your system for leftover files and folders associated with Flash Player, allowing you to remove them.
- Before using any third-party uninstaller, it’s crucial to back up your data to avoid accidental file deletion.
Flash Player Alternatives
Flash Player’s demise has paved the way for a new era of web development, relying on more efficient and secure technologies. While Flash was once the dominant force, its vulnerabilities and lack of cross-platform compatibility led to its downfall.
Now, developers have access to a diverse range of alternatives that offer improved performance, security, and user experiences.
HTML5 and its Capabilities
HTML5, the latest version of the language that defines the structure and content of web pages, has emerged as the leading alternative to Flash Player. It offers a rich set of features that enable developers to create interactive, engaging, and dynamic web content without relying on external plugins.
HTML5’s capabilities extend to multimedia, graphics, animation, and even gaming, making it a versatile solution for modern web development.
JavaScript Libraries for Interactive Experiences
JavaScript libraries, such as jQuery, React, and Angular, provide powerful tools for building interactive web applications. These libraries simplify the development process, allowing developers to create complex user interfaces, handle dynamic content updates, and implement interactive features without the need for Flash.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternatives, Adobe Flash Player is dead Here’s how to remove it from your Mac.
- HTML5
- Advantages:Open standard, cross-platform compatibility, improved performance, security enhancements, and support for multimedia content.
- Disadvantages:Limited support for older browsers, potential for compatibility issues across different devices, and a steeper learning curve for some developers.
- JavaScript Libraries
- Advantages:Extensive functionality, improved performance, active community support, and a wide range of available libraries.
- Disadvantages:Complex syntax, potential for performance bottlenecks, and a steep learning curve for beginners.
Successful Transitions from Flash to HTML5
Several prominent websites have successfully transitioned from Flash to HTML5, demonstrating the effectiveness of these alternatives.
- YouTube:Once heavily reliant on Flash, YouTube transitioned to HTML5 for its video player, improving performance and user experience across various devices. This move also addressed security concerns associated with Flash.
- Facebook:Facebook’s transition from Flash to HTML5 for its game platform significantly enhanced the user experience, allowing for smoother gameplay and faster loading times.
- Netflix:Netflix’s transition to HTML5 for its streaming platform provided a more secure and reliable experience for users, while also improving compatibility across different devices.
Impact on Web Development
The removal of Flash Player has significantly impacted web development practices, forcing a shift towards HTML5 and other modern technologies. This transition has presented both challenges and opportunities for web designers and developers.
Adapting to New Technologies
The demise of Flash has spurred a widespread adoption of HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. These technologies offer a more robust, secure, and platform-independent approach to web development. Web designers and developers have had to adapt their skills and workflows to incorporate these new technologies.
- HTML5:This markup language provides a comprehensive set of features for creating interactive and dynamic web content, including multimedia support, offline storage, and enhanced user interface elements.
- CSS3:This styling language offers advanced features for creating visually appealing and responsive web designs. It allows for more precise control over layout, typography, and animation, enhancing the user experience.
- JavaScript:This programming language is essential for adding interactivity and dynamic functionality to websites. It is used to create animations, handle user input, and communicate with web servers.
Redesigning Websites
Many websites that relied heavily on Flash have undergone significant redesigns to remove Flash content and implement HTML5 alternatives. This has resulted in improved performance, security, and accessibility for users.
Adobe Flash Player is officially dead, and it’s time to give your Mac a spring cleaning. Removing Flash is a good first step, but you should also think about disinfecting your entire setup. You can find some helpful tips on how to disinfect your Mac, iPhone, mouse, trackpad, keyboard, and cases at How to disinfect your Mac, iPhone, mouse, trackpad, keyboard and cases.
This will help you keep your devices clean and germ-free, and it’s a good idea to do it regularly, especially if you share your devices with others. Once you’ve disinfected your devices, you can rest assured that your Mac is free of Flash and any lingering germs.
- YouTube:The popular video-sharing platform transitioned from Flash to HTML5, resulting in smoother playback, reduced buffering, and improved performance across various devices.
- Facebook:Facebook’s redesigned website utilizes HTML5 and JavaScript to create a more interactive and engaging user experience. This transition has led to faster loading times and improved performance on mobile devices.
- Adobe:Adobe itself has redesigned its website and applications to rely on HTML5, showcasing the company’s commitment to the future of web development.
Legacy Content and Flash Games
The end of Flash Player has left a significant void in the world of online content. Millions of websites and games still rely on this technology, and accessing them now poses a challenge. While many websites have migrated to HTML5, a considerable amount of legacy content remains inaccessible without Flash Player.The transition away from Flash has created a need to preserve and emulate Flash games and other content.
This ensures that users can still access and enjoy this content, even though Flash Player is no longer supported.
Efforts to Preserve Flash Content
Several initiatives are underway to preserve and emulate Flash content. These efforts aim to ensure that users can still access and enjoy this content in the future.
- Ruffleis an open-source Flash Player emulator that allows users to play Flash games and view Flash content in modern web browsers. It is actively developed and supported by a community of developers. Ruffle works by translating Flash bytecode into JavaScript, enabling it to run in web browsers that do not have Flash Player installed.
- BlueMaxima’s Flashpointis a non-profit project that aims to preserve Flash games and other content by creating an archive of Flash files. This archive can be accessed through a dedicated software application that allows users to play Flash games and view Flash content in a safe and secure environment.
Flashpoint provides a curated collection of Flash games and other content, making it a valuable resource for those seeking to revisit their favorite Flash experiences.
Resources for Accessing Flash Content
Several resources are available for users who wish to access or play Flash content. These resources offer various methods for accessing legacy Flash content, including emulators, archives, and dedicated websites.
So, Flash Player is officially dead. It’s time to give your Mac a spring cleaning and get rid of that outdated software. While you’re at it, you might want to check out How to add a stack of recent documents to your Mac’s Dock to keep your frequently used files right at your fingertips.
Once you’ve removed Flash Player, your Mac will be running smoother and you’ll be ready to tackle any new projects.
- Flashpointoffers a comprehensive archive of Flash games and other content, providing a dedicated platform for accessing this content. Users can download the Flashpoint software application and access the archive’s extensive collection of Flash experiences.
- Ruffle, an open-source Flash Player emulator, allows users to play Flash games and view Flash content in modern web browsers. Ruffle can be accessed as a browser extension or through a dedicated website, providing users with a convenient way to experience legacy Flash content.
- Internet Archive, a non-profit digital library, has a collection of Flash games and other content that can be accessed through its website. The Internet Archive’s collection provides a valuable resource for those seeking to explore and experience legacy Flash content.
The Future of Web Technologies: Adobe Flash Player Is Dead Here’s How To Remove It From Your Mac.
The demise of Flash Player marked a significant turning point in the evolution of web technologies. This event ushered in a new era characterized by advancements in web standards, the rise of emerging technologies, and a renewed focus on user experience.
Web Standards and Advancements
The departure of Flash Player accelerated the adoption and refinement of web standards, particularly HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. These technologies offer a more robust and secure platform for developing interactive web content. HTML5 provides a comprehensive framework for multimedia, graphics, and animation, eliminating the need for external plugins.
CSS3 enables sophisticated styling and visual effects, enhancing the aesthetics and user experience of web pages. JavaScript, a versatile scripting language, empowers developers to create dynamic and interactive web applications.
Emerging Technologies
The web landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to shape the future of web development.
- WebAssembly: A low-level language that enables developers to compile code written in languages like C, C++, and Rust to run efficiently in web browsers. WebAssembly offers significant performance gains and expands the possibilities for web applications.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs combine the best features of web applications and native mobile apps. They offer offline functionality, push notifications, and seamless integration with the device’s operating system.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is increasingly being integrated into web applications, enabling features such as personalized recommendations, intelligent search, and automated tasks.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies are opening new avenues for immersive and interactive web experiences. Web developers are exploring ways to integrate these technologies into websites and applications.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management solutions, which are finding applications in web development for decentralized applications (dApps) and secure data storage.
The Future of Web Design and User Experience
The future of web design and user experience is characterized by a focus on accessibility, personalization, and seamless user interactions.
- Accessibility: Web designers are prioritizing accessibility, ensuring that websites and applications are usable by individuals with disabilities. This includes incorporating features like screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and color contrast adjustments.
- Personalization: Web experiences are becoming increasingly personalized, with websites and applications tailoring content and functionality to individual user preferences. This is achieved through data analysis, machine learning, and user behavior tracking.
- Seamless User Interactions: The emphasis is on creating seamless and intuitive user experiences. This involves designing intuitive interfaces, optimizing for mobile devices, and leveraging emerging technologies like voice interfaces and gesture recognition.
Conclusion: A New Era of Web Development
The demise of Adobe Flash Player marks a significant turning point in the evolution of web technologies. Flash’s dominance is now a thing of the past, paving the way for a more secure, performant, and innovative web experience.
Impact on Web Development
The shift away from Flash has had a profound impact on web development practices. Developers are now embracing HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript as the core technologies for building interactive and engaging web experiences. This transition has led to a number of benefits:
- Enhanced Security:HTML5 is inherently more secure than Flash, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and exploits. This is crucial for protecting user data and ensuring a safe browsing experience.
- Improved Performance:HTML5 applications are generally faster and more efficient than Flash-based content, resulting in a smoother user experience, especially on mobile devices.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:HTML5 is designed to work seamlessly across different platforms and devices, eliminating the need for separate development efforts for various operating systems.
- Open Standards:HTML5 is an open web standard, allowing developers to build applications without relying on proprietary software or plugins.
Staying Up-to-Date with Web Technologies
The rapid pace of technological advancements in the web development landscape emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and adaptation. Developers must stay abreast of the latest trends and technologies to create modern, secure, and engaging web experiences. This can be achieved through:
- Attending industry conferences and workshops:These events provide valuable insights into the latest developments and best practices.
- Engaging with online communities and forums:Online platforms offer opportunities to connect with other developers, share knowledge, and learn from their experiences.
- Reading industry publications and blogs:Staying informed about the latest trends and technologies is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
- Experimenting with new technologies:Hands-on experience is essential for understanding the capabilities and limitations of emerging technologies.
Concluding Remarks
The demise of Flash Player marks a significant shift in the web development landscape. While it’s a goodbye to a familiar technology, it’s also a welcome change that paves the way for a more secure, performant, and accessible web experience.
So, as you say farewell to Flash Player, embrace the future of web technologies and enjoy the smooth sailing that HTML5 offers.
FAQs
Is it safe to remove Flash Player from my Mac?
Yes, it’s safe and recommended to remove Flash Player from your Mac. Adobe has discontinued support for Flash Player, and it’s no longer considered secure. Removing it will help protect your Mac from potential security risks.
What if I have websites that still require Flash Player?
Many websites have transitioned away from Flash Player, but if you encounter a site that still requires it, you can try using an alternative browser or contact the website’s developers to see if they have an HTML5 version available.
Will removing Flash Player affect my Mac’s performance?
Removing Flash Player should not have a significant impact on your Mac’s performance. In fact, it may even improve performance, as Flash Player was known to consume resources and sometimes cause slowdowns.