How To Free Up Disk Space In Macos High Sierra
How to free up disk space in macOS High Sierra – Feeling cramped on your macOS High Sierra drive? You’re not alone. As your Mac stores more apps, files, and data, it can start to feel sluggish and even run out of space. This guide will walk you through the best ways to free up disk space, giving you a smoother, faster, and more efficient macOS experience.
From identifying and removing unnecessary files to optimizing system settings, we’ll cover all the essential steps for reclaiming your hard drive. You’ll learn how to analyze your disk space usage, identify culprits like large files and system caches, and effectively manage your data.
We’ll even explore third-party tools that can help streamline the process.
Understanding Disk Space Usage
It’s super annoying when your Mac starts feeling sluggish and you can’t install new apps because you’re running out of disk space. But don’t worry, figuring out what’s hogging your drive isn’t rocket science. We’ll break down how to identify the culprits and reclaim your precious gigabytes.
Disk Space Usage Analysis
macOS High Sierra provides built-in tools to help you understand where your disk space is going. These tools give you a visual representation of your storage usage, making it easy to pinpoint the biggest space consumers.
Using the Finder
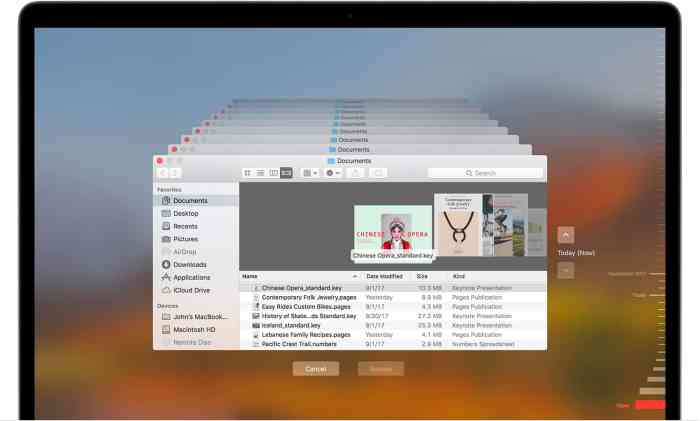
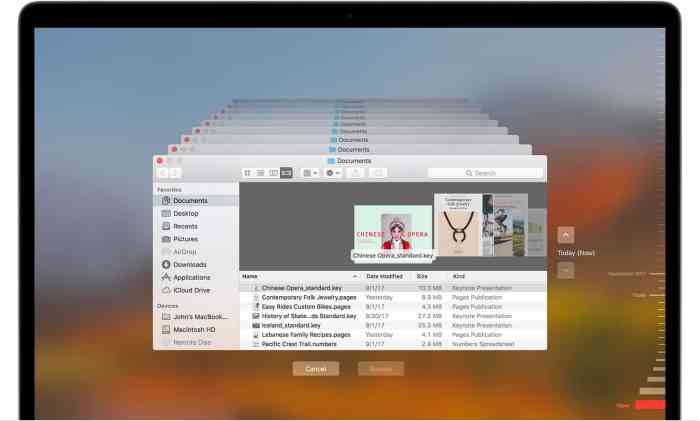
The Finder, your trusty file explorer, can give you a quick overview of your disk space usage. Here’s how:
- Open a Finder window.
- Click on the “Go” menu in the menu bar.
- Select “About This Mac.”
- Click on the “Storage” tab.
- The “Storage” tab displays a pie chart that visually represents the storage usage on your Mac.
Using Disk Utility
For a more detailed breakdown of your disk space usage, Disk Utility is your go-to tool. Here’s how to use it:
- Open “Launchpad” and search for “Disk Utility.”
- In Disk Utility, select your startup disk (usually named “Macintosh HD”).
- Click on the “First Aid” tab.
- Click on “Run” to scan your disk for errors.
- Once the scan is complete, click on the “Storage” tab.
- This tab provides a detailed breakdown of your disk space usage by file type, including system files, applications, and user data.
Typical Disk Space Consumption
Here’s a table that provides a general overview of typical disk space consumption by different file types:| File Type | Typical Disk Space Consumption ||—|—|| System Files| 10-20 GB || Applications| Varies greatly depending on the number and size of installed apps || User Data| Can range from a few GB to hundreds of GB, depending on your usage habits || Photos and Videos| Can consume significant amounts of disk space, especially high-resolution images and videos || Music and Audio Files| Can consume a large amount of disk space, especially if you have a large music library || Downloads| Can quickly accumulate and consume a significant amount of disk space || Other Files| Includes documents, emails, and other files you’ve downloaded or created |
Identifying and Removing Unnecessary Files
You’ve identified the space hogs, now it’s time to clean house! We’ll use the Finder to locate and delete large files or folders, leverage Disk Utility to find and remove duplicate files, and then empty the Trash and Downloads folder to complete the process.
Using the Finder to Locate and Delete Large Files or Folders, How to free up disk space in macOS High Sierra
The Finder is your go-to tool for managing files and folders. To identify and delete large files or folders, follow these steps:
- Open the Finder.
- Click on “Go” in the menu bar.
- Select “Applications”.
- Locate the application that is taking up the most space and move it to the Trash. You can also move large files or folders to the Trash.
Using Disk Utility to Identify and Remove Duplicate Files
Disk Utility is a powerful tool built into macOS that can help you identify and remove duplicate files. Duplicate files can take up a lot of space, so it’s a good idea to check for them regularly.
- Open Disk Utility. You can find it in the Applications folder under Utilities.
- Select the hard drive you want to scan for duplicates.
- Click on the “First Aid” tab.
- Click on “Verify Disk”. This will check your hard drive for errors.
- If Disk Utility finds any errors, click on “Repair Disk” to fix them.
Disk Utility can also help you identify and remove duplicate files. To do this, you can use a third-party app like Gemini 2, which can scan your entire hard drive for duplicate files and help you remove them.
Emptying the Trash and Clearing the Downloads Folder
The Trash and Downloads folder are two common areas where unnecessary files can accumulate. To free up space, empty the Trash and clear the Downloads folder regularly.
- Select the Trash icon on your dock.
- Click on “Empty Trash” to permanently delete all the files in the Trash.
- Open your Downloads folder.
- Delete any files you no longer need.
Optimizing System Files and Applications
Optimizing system files and applications can free up significant disk space on your macOS High Sierra system. This involves managing system caches and logs, uninstalling unused applications, and removing associated files.
Managing System Caches and Logs
System caches and logs are temporary files that your Mac uses to speed up operations and record system events. Over time, these files can accumulate and take up valuable disk space. Regularly clearing them can help free up space.
“Caches are temporary files that store data that is frequently used to speed up access to information.”
- System Cache:The system cache stores data that is frequently accessed by applications, such as recently opened documents, app settings, and web browsing history. You can clear the system cache by restarting your Mac. This will force the system to rebuild the cache from scratch.
- User Cache:The user cache stores data specific to your user account, such as browser history, application preferences, and temporary files. You can clear the user cache by going to the Library folder in your user directory and deleting the Caches folder.
- Logs:System logs are text files that record system events, such as errors, warnings, and system activity. You can clear the system logs by going to the Console application in the Utilities folder.
Uninstalling Unused Applications and Removing Associated Files
Unused applications take up disk space and can clutter your system. Uninstalling them and removing associated files can free up space.
- Uninstalling Applications:You can uninstall applications using the Applications folder in Finder or by dragging the application to the Trash.
- Removing Associated Files:When you uninstall an application, some files may remain on your system, such as preferences, support files, and data files. These files can be found in the Library folder in your user directory.
Deleting Common System Files
Some system files can be safely deleted to free up space. However, it’s crucial to exercise caution, as deleting essential files can cause system instability.
- Temporary Files:Temporary files are created by applications and the system to store data temporarily. You can delete temporary files by going to the Library folder in your user directory and deleting the Temporary Items folder.
- Downloaded Files:Downloaded files, such as software installers, documents, and media files, can take up significant space. You can delete downloaded files by going to the Downloads folder in Finder.
Managing User Data
Your user data, including documents, photos, videos, and other files, can take up a significant amount of disk space. Managing your user data effectively is crucial for freeing up space on your macOS High Sierra system.
Compressing Large Files or Folders
Compressing large files or folders can reduce their size, freeing up disk space. macOS High Sierra includes the Archive Utility, a built-in tool for creating compressed archives.
- To compress a file or folder, select the item and right-click (or Control-click).
- Choose “Compress [item name]” from the context menu.
- The Archive Utility will create a compressed archive file with a .zip extension.
- You can then delete the original file or folder, saving space on your disk.
You can also use third-party compression tools like 7-Zip or WinRAR, which offer additional features and compression formats.
Storing User Data in Cloud Services
Cloud storage services, like iCloud, provide a convenient way to store your data online, freeing up space on your local drive.
- iCloud offers 5GB of free storage, but you can purchase additional storage if needed.
- With iCloud, you can store documents, photos, videos, and other files.
- Files stored in iCloud are accessible from your Mac, iOS devices, and even your web browser.
- By storing data in iCloud, you can access it from any device and free up disk space on your Mac.
Other cloud storage services, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive, offer similar features.
Organizing and Deleting Old or Unnecessary Photos, Videos, and Documents
Regularly organizing and deleting old or unnecessary photos, videos, and documents can significantly free up disk space.
- Use the Photos app to organize your photo library. You can create albums, delete duplicates, and edit photos to reduce their file size.
- The Photos app also includes features for automatically deleting duplicate photos and videos.
- Review your documents and delete any that are no longer needed.
- Use the “Recently Added” or “Recently Opened” sections in Finder to identify files you haven’t accessed recently.
Deleting old or unnecessary files can significantly reduce the amount of disk space they occupy.
Alright, so you’re trying to free up some space on your Mac, right? Sometimes it feels like you’re constantly running out of room. You might want to check out this article on fixing battery drain and GPS issues after updating to iOS 14 and watchOS 7: Fix battery drain, missing GPS data after updating to iOS 14, watchOS 7.
Anyway, back to your Mac. Deleting old files and apps is a good start, but if you’re still struggling, there are some other tricks you can try. Good luck!
Utilizing Third-Party Tools: How To Free Up Disk Space In MacOS High Sierra
Sometimes, even after diligently cleaning up your Mac, you might find yourself needing a little extra help to free up disk space. That’s where third-party tools come in handy. These applications offer a wide range of features designed to optimize your Mac’s storage and performance.
Comparing Disk Space Management Applications
Disk space management applications can be categorized into two main types: disk cleanup tools and data recovery tools.
- Disk cleanup tools are designed to scan your Mac for unnecessary files, duplicates, and other data that can be safely removed to free up space. They typically offer features such as:
- Identifying and removing large files and folders
- Deleting temporary files and system caches
- Finding and removing duplicate files
- Uninstalling unwanted applications
- Analyzing disk usage and providing insights into storage consumption
- Data recovery tools, on the other hand, are designed to retrieve lost or deleted files from your Mac’s storage. They work by scanning your hard drive for traces of deleted files and attempting to recover them. These tools can be incredibly useful if you accidentally delete an important file or if your Mac experiences a system crash.
- Data recovery tools can recover files from various sources, including the trash bin, external drives, and even damaged hard drives.
- They often offer different recovery modes, such as “Quick Scan” for recently deleted files and “Deep Scan” for files that have been deleted longer ago.
- Some data recovery tools can also recover files from formatted drives or drives that have been corrupted.
Benefits of Using a Dedicated Disk Cleanup Tool
Using a dedicated disk cleanup tool can significantly benefit your Mac’s performance and storage management. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Automated cleaning:Disk cleanup tools automate the process of identifying and removing unnecessary files, saving you time and effort.
- Comprehensive analysis:They provide detailed insights into your disk usage, helping you understand where your storage space is being consumed.
- Advanced features:Many disk cleanup tools offer advanced features such as duplicate file detection, system optimization, and even data compression.
- Improved performance:By freeing up disk space and optimizing system files, disk cleanup tools can improve your Mac’s overall performance and responsiveness.
Data Recovery Tools
Data recovery tools are essential for retrieving lost or deleted files from your Mac’s storage. These tools use sophisticated algorithms to scan your hard drive for traces of deleted files and attempt to recover them.
- Types of data recovery tools:Data recovery tools come in various forms, from free basic tools to advanced professional software. Some popular options include:
- Disk Drill:A versatile data recovery tool that supports various file systems and offers a free version with limited recovery capabilities.
So, you’re trying to free up some space on your Mac, huh? You’re not alone. A lot of people find themselves running out of space on their Macs, especially if they’re using High Sierra. One way to free up space is to get rid of old files you don’t need anymore.
Another option is to take a break from all the computer stuff and learn to play a musical instrument with iOS ! It’s a great way to relax and be creative. Once you’re done, you can get back to your Mac and try some of those other space-saving tips.
- Stellar Data Recovery:A professional-grade data recovery tool with advanced features for recovering lost files from formatted or corrupted drives.
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard:A user-friendly data recovery tool that offers a free trial and various recovery modes for different scenarios.
- Disk Drill:A versatile data recovery tool that supports various file systems and offers a free version with limited recovery capabilities.
- Features of data recovery tools:
- File preview:Most data recovery tools allow you to preview recovered files before restoring them, ensuring you recover the correct data.
- File filtering:You can filter recovered files based on file type, size, and other criteria to narrow down your search.
- Data recovery from various sources:Data recovery tools can recover files from various sources, including the trash bin, external drives, and even damaged hard drives.
Additional Tips and Techniques
Beyond the essential steps of identifying and removing unnecessary files, optimizing system files and applications, and managing user data, there are additional tips and techniques that can help you further optimize your macOS High Sierra system and reduce disk space usage.
These techniques can improve system performance and make your Mac run smoother.
Freeing up disk space in macOS High Sierra can be a pain, especially if you’re trying to keep your downloads and apps organized. Sometimes, you might need to clear out old files or move them to an external drive.
If you’re using your iPhone or iPad, you might want to check out how to change the size of picture-in-picture windows to make sure your video calls aren’t taking up too much space on your screen. Once you’ve cleared some space on your Mac, you can download and install all the new apps you want!
Creating a Bootable USB Drive
Creating a bootable USB drive allows you to reinstall macOS High Sierra, repair your system, or even upgrade to a newer version. This is a valuable tool for troubleshooting and maintaining your Mac.
- Connect a USB drive with at least 8GB of free space to your Mac.
- Open the Disk Utility application, which you can find in the Applications folder, then Utilities folder.
- Select the USB drive in the Disk Utility window.
- Click the “Erase” button and format the drive as “Mac OS Extended (Journaled)” with a suitable name.
- Download the macOS High Sierra installer from the Mac App Store.
- Open the “Terminal” application (Applications > Utilities > Terminal).
- Run the following command, replacing “macOS High Sierra Installer.app” with the actual name of the installer file:
sudo /Applications/Install\ macOS\ High\ Sierra.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia--volume /Volumes/USB_Name --applicationpath /Applications/Install\ macOS\ High\ Sierra.app --nointeraction - Enter your administrator password when prompted.
- Wait for the process to complete, which may take some time.
Once complete, you have a bootable USB drive that can be used to reinstall or upgrade macOS.
Using an External Hard Drive for Data Backup and Storage
External hard drives provide a safe and reliable way to back up your data and free up space on your Mac’s internal drive.
- Data Backup:Regular backups protect your valuable data from accidental deletion, hardware failures, or other unforeseen events. Consider using Time Machine, Apple’s built-in backup tool, to automatically back up your data to an external hard drive.
- Storage:External hard drives can be used to store large files, such as videos, photos, and music, that you don’t need to access frequently. This can help free up space on your Mac’s internal drive.
Using an external hard drive for backup and storage offers peace of mind and can significantly improve your Mac’s performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after freeing up disk space, you might encounter issues related to storage. This section will cover common error messages and troubleshooting steps to address them.
Error Messages and Their Meanings
Understanding error messages is crucial for troubleshooting. Here are some common error messages and their explanations:
“There is not enough disk space available to complete this operation.”
This indicates that your system lacks sufficient storage for the requested task, such as installing an application or saving a file.
“The disk is full.”
This straightforward message signifies that your disk has reached its storage capacity.
“Error writing to disk.”
This message suggests a problem with your disk’s ability to write data, potentially caused by a faulty drive or a corrupted file system.
“Disk Utility cannot repair the disk.”
This message indicates a serious problem with your disk’s file system, potentially requiring data recovery services or disk replacement.
Troubleshooting Steps
Here are some general steps to troubleshoot disk space issues in macOS High Sierra:
- Check Disk Space:Use the “About This Mac” window to view your disk space usage. This will help identify the culprit behind your storage limitations.
- Restart Your Mac:A simple restart can often resolve temporary issues that may be causing disk space problems.
- Run Disk Utility:Disk Utility is a built-in tool that can repair disk errors and optimize your storage. You can access it by going to “Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility.”
- Empty Trash:Regularly empty your trash to remove unwanted files and reclaim disk space.
- Check for Large Files:Use Finder’s “Get Info” option to identify large files that might be consuming unnecessary storage.
- Uninstall Unused Applications:Remove applications you no longer use to free up space.
- Use Time Machine Backups:Ensure your Time Machine backups are not taking up excessive storage. You can adjust your backup settings to limit the storage used.
- Check for Hidden Files:Some hidden files can consume significant storage. Use a utility like “CleanMyMac X” to identify and remove these files.
- Contact Apple Support:If you’re still facing issues, consider contacting Apple Support for further assistance.
Specific Error Codes and Scenarios
Here are some common error codes and scenarios you might encounter:
- Error Code-1000: This code typically indicates a problem with the disk itself. It might be failing or corrupted. Consider backing up your data and contacting Apple Support or a data recovery service.
- Error Code-1001: This code usually points to a problem with the file system on your disk. Disk Utility can often repair this error. If not, you might need to reformat the disk, potentially losing data.
- “The disk you inserted was not readable”:This message indicates a problem with the external drive you’re trying to access. Try connecting it to a different port or using a different cable. If the problem persists, the drive might be failing.
- “Your startup disk is full”:This message means your main system drive has run out of space. You’ll need to free up space on this drive to continue using your Mac.
Maintaining Disk Space
You’ve done a great job freeing up disk space on your Mac, but it’s important to maintain those gains and prevent future space issues. Think of it like a spring cleaning – you’ve decluttered once, but you need to keep up with it to stay organized.
This section will help you establish good habits for managing your Mac’s storage space.
Regularly Monitoring Disk Space Usage
Regularly checking your disk space usage helps you stay ahead of potential issues. You can monitor your disk space in a few ways:
- Use the Apple Menu:Click the Apple icon in the top-left corner of your screen, then select “About This Mac.” Click on the “Storage” tab to see a visual representation of your disk space usage. This will give you a quick overview of how much space is available and where it’s being used.
- Utilize Disk Utility:Open Disk Utility (located in Applications > Utilities) and select your startup disk. Click the “First Aid” tab to check for errors and optimize your disk, and the “Storage” tab to see a more detailed breakdown of your disk space usage.
- Install Third-Party Apps:Several third-party apps, like CleanMyMac X or DaisyDisk, offer more in-depth analysis and cleaning options for your disk space.
Creating a Backup Plan
It’s crucial to have a backup plan in place to protect your data. If your Mac’s hard drive fails, you’ll be glad you have a backup. Here are some backup options:
- Time Machine:This is Apple’s built-in backup solution, and it’s a great option for most users. It automatically backs up your entire Mac to an external drive, allowing you to restore files or your entire system if needed.
- Cloud Storage:Services like iCloud, Google Drive, or Dropbox can be used to back up your files online. This is a good option if you want to access your data from multiple devices or if you’re concerned about losing your external drive.
- External Hard Drives:You can also back up your data to an external hard drive. This is a more affordable option than cloud storage, but you need to physically store the drive.
Optimizing System Settings
You can make adjustments to your system settings to prevent future disk space issues:
- Reduce Mail Downloads:In Mail preferences, limit the number of messages downloaded to your Mac. This will reduce the amount of space used by your email.
- Enable “Optimize Storage” in iCloud Settings:This feature will automatically remove files from your Mac that are stored in iCloud. This can free up significant space, especially if you have a lot of photos or videos stored in iCloud.
- Disable “Automatic Downloads” in App Store Preferences:Prevent apps from automatically downloading updates, saving you disk space and bandwidth.
Summary
By taking control of your disk space, you’re not only freeing up valuable storage but also ensuring your macOS High Sierra runs smoothly and efficiently. Regularly cleaning up your drive and adopting good data management practices will keep your Mac in tip-top shape, allowing you to focus on what matters most – enjoying your favorite apps and content without performance hiccups.
Commonly Asked Questions
How do I check my available disk space?
You can easily check your available disk space by going to the Apple menu, selecting “About This Mac,” and then clicking on the “Storage” tab.
What are some common causes of disk space depletion?
Common causes include large files like photos and videos, app caches, system logs, and downloads.
Is it safe to delete system files?
Be cautious when deleting system files. Only delete files that you’re sure are safe to remove. Always back up your data before making any major changes.
Can I use a third-party disk space management tool?
Yes, there are many third-party tools available that can help you analyze and manage your disk space. Some popular options include CleanMyMac X and DaisyDisk.