How To Perform A Manual Mac System Migration
How To Perform a Manual Mac System Migration is a process that can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a smooth transition. Whether you’re upgrading to a new Mac, moving to a different operating system, or simply need to transfer data from one machine to another, a manual migration can offer greater control and flexibility than automated methods.
This guide will walk you through the entire process, from preparing your old system to verifying the successful migration on your new one. We’ll cover essential tasks like backing up your data, creating a bootable USB drive, and transferring applications, settings, and user files.
You’ll also learn about different migration methods, security considerations, and tips for a stress-free experience.
Preparing for the Migration
Before diving into the migration process, it’s crucial to prepare your Mac and ensure a smooth transition. This includes backing up your data and system configuration, creating a bootable USB drive, and understanding the potential challenges you might encounter.
Backing Up Your Data and System Configuration
A comprehensive backup is essential before starting any migration. This safeguards your data and system configuration in case something goes wrong. You can choose from several backup methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Time Machine: Apple’s built-in backup solution, Time Machine, is an excellent choice for creating incremental backups of your entire system. It automatically saves snapshots of your data and system settings, allowing you to restore your Mac to a previous state if needed.
- Third-Party Backup Software: Several third-party backup applications offer more advanced features, such as granular file selection, cloud storage integration, and scheduling options. Some popular options include Carbon Copy Cloner, SuperDuper!, and Acronis True Image.
- External Hard Drive: A simple yet effective method is to manually copy your data to an external hard drive. This provides a direct backup of your files, but it doesn’t include system settings or applications.
Creating a Bootable USB Drive for Installing macOS
A bootable USB drive is necessary to install macOS on your new Mac. This drive contains the macOS installer, allowing you to start the installation process without relying on the existing operating system.
- Download macOS Installer: Visit the Mac App Store and download the macOS installer for the version you want to install. This will create a DMG file containing the installation files.
- Prepare USB Drive: Connect a USB drive with at least 8GB of free space to your Mac. Format the drive using Disk Utility, selecting the “macOS Extended (Journaled)” format. This ensures the drive is compatible with the macOS installer.
- Create Bootable Drive: Open Terminal and run the following command, replacing “path/to/macOS.dmg” with the actual path to the macOS installer file and “/Volumes/USB_Drive” with the name of your USB drive:
sudo /Applications/Install\ macOS\ Ventura.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia--volume /Volumes/USB_Drive --applicationpath /path/to/macOS.dmg
Migrating User Data
The next step in your Mac system migration is moving your user data. This is the heart of your system, containing everything from your documents and photos to your applications and settings. We’ll explore different methods for transferring your data, comparing their advantages and disadvantages, and providing a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth transition.
Methods for Transferring User Data
There are several ways to move your user data to your new Mac. Each method has its own pros and cons, so choosing the right one depends on the size and type of your data, your comfort level with technology, and your time constraints.
- External Drives: Using an external hard drive is a classic and reliable method for transferring large amounts of data. You can simply copy your entire user folder or specific files and folders to the drive, then transfer them to your new Mac.
- Pros: External drives offer high transfer speeds and are relatively inexpensive. They provide a physical backup of your data, making them a good choice for safeguarding important files.
- Cons: External drives require an extra step to copy data and can be time-consuming for large datasets. They also present a potential security risk if not properly secured.
- Cloud Services: Cloud storage services like iCloud, Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive allow you to store your data online and access it from any device. You can use these services to sync your files and folders between your old and new Macs.
- Pros: Cloud services are convenient, offering easy access to your data from anywhere. They often provide automatic syncing and version history, ensuring your data is up-to-date and backed up.
- Cons: Cloud services can be slow for transferring large amounts of data, especially if you have a limited internet connection. You’ll need a paid subscription for larger storage capacities, and there are security concerns about storing sensitive data online.
- Network Transfers: If both your old and new Macs are connected to the same network, you can use a network transfer method like AirDrop or a file-sharing program like File Sharing to move your data.
- Pros: Network transfers are fast and convenient, especially for smaller files.
They don’t require any external hardware or cloud subscriptions.
- Cons: Network transfers can be unreliable if your network connection is unstable. They may not be suitable for transferring large amounts of data due to potential speed limitations.
- Pros: Network transfers are fast and convenient, especially for smaller files.
Step-by-Step Guide to Transferring User Data
Once you’ve chosen your preferred method, follow these steps to transfer your user data:
- Backup Your Data: Before starting any transfer, create a backup of your entire system using Time Machine or another backup solution. This is crucial in case anything goes wrong during the migration process.
- Select Your Transfer Method: Based on the size and type of your data, your comfort level, and your time constraints, choose the most appropriate method for transferring your data.
- Prepare Your Destination: Ensure your new Mac has enough storage space for your data. If using an external drive, format it properly and make sure it’s connected to both Macs. If using cloud services, verify your account has sufficient storage space and is set up for syncing.
- Transfer Your Files: Depending on your chosen method, follow the specific instructions for transferring your files. For example, if using an external drive, copy the entire user folder or specific files and folders to the drive. If using cloud services, upload your data to the service and ensure it’s synced to your new Mac.
Moving your Mac’s operating system manually can be a bit of a hassle, especially if you’re not familiar with the process. But if you’re ever stuck on a step and need a quick answer, you can always check out this article on how to look up anything with one tap on Mac.
It’s a super helpful resource that can save you tons of time and frustration. Once you’ve got the basics down, you’ll be able to move your Mac’s system like a pro!
- Transfer Your Applications: Some applications may be automatically transferred during the migration process. However, others may need to be downloaded and installed separately. Refer to the application’s website or documentation for specific instructions.
- Transfer Your Settings: Some settings, like your desktop background, browser bookmarks, and email accounts, may be transferred automatically.
Others may require manual configuration. Check your settings and make any necessary adjustments on your new Mac.
Migrating Applications: How To Perform A Manual Mac System Migration
Moving your applications from your old Mac to your new one is an important part of the migration process. You’ll need to figure out which applications you want to transfer, how to move them, and how to ensure they work correctly on your new system.
Identifying and Transferring Applications
It’s important to identify which applications you need to transfer before you start the migration process. You can do this by looking at the Applications folder on your old Mac and checking for any programs you use regularly. You can also use the “Applications” section of your Mac’s System Preferences to see a list of installed applications.Once you’ve identified the applications you want to transfer, you have a few options:
- Reinstall from the original installer:Many applications can be reinstalled from their original installers. This is a good option if you have the original installation media or if you’ve downloaded the installer from the application’s website.
- Use a migration tool:Apple’s Migration Assistant can transfer applications from your old Mac to your new one. However, it may not transfer all applications, and it may require you to reactivate some applications after the migration.
- Manually copy the application files:You can manually copy the application files from your old Mac to your new one. This is a more advanced option, and it’s important to make sure you copy all of the necessary files.
Migrating Applications Requiring Specific Licenses or Configurations
Some applications require specific licenses or configurations. You may need to reactivate these applications after the migration.
- Check the application’s website for instructions:Many application developers provide instructions on how to reactivate their applications after a system migration.
- Contact the application’s support team:If you can’t find instructions on the application’s website, you can contact the application’s support team for help.
- Transfer license files:Some applications store their licenses in separate files. You can transfer these files to your new Mac to reactivate the application.
Managing Application Dependencies and Compatibility Issues
Applications may depend on other applications or system components. It’s important to make sure that all of the necessary dependencies are installed on your new Mac.
- Check the application’s website for system requirements:Before you migrate an application, check the application’s website to see if it’s compatible with your new Mac’s operating system.
- Install any necessary dependencies:If the application requires any specific dependencies, make sure to install them on your new Mac before you migrate the application.
- Test the application after migration:After you’ve migrated an application, it’s important to test it to make sure it works correctly.
Migrating System Settings
System settings encompass various aspects of your Mac’s operation, including user accounts, preferences, and network configurations. Transferring these settings ensures a seamless transition to your new Mac.
User Accounts
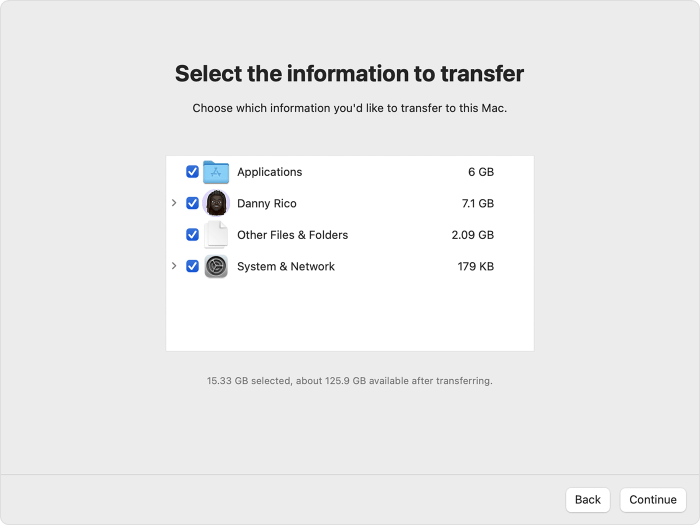
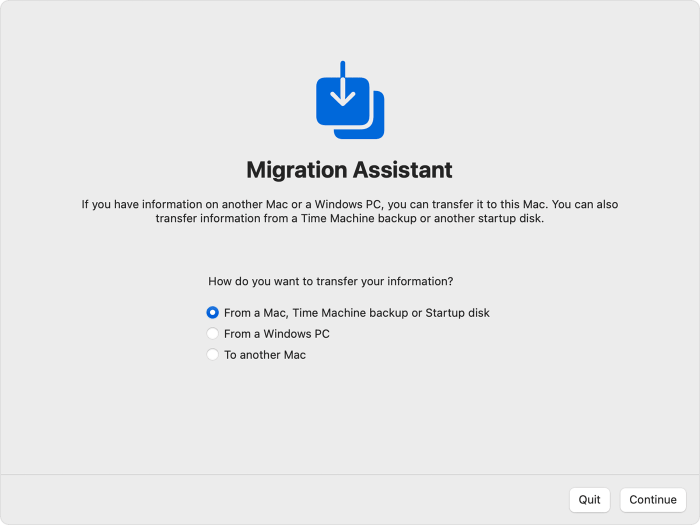
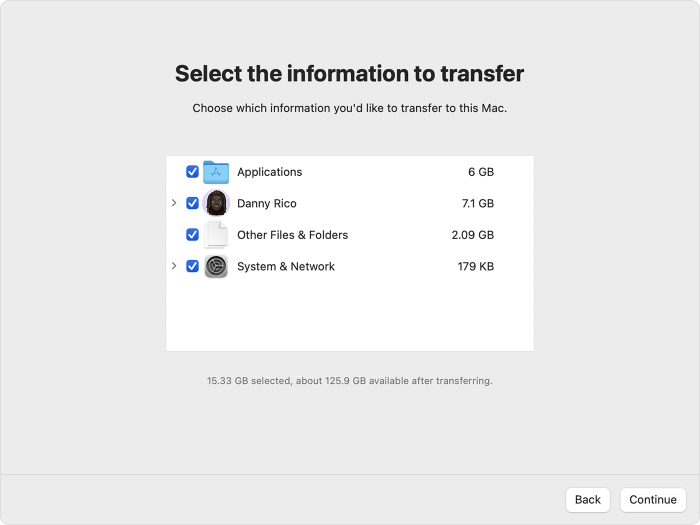
Migrating user accounts allows you to retain your personalized settings, such as desktop backgrounds, dock layouts, and application preferences. To migrate user accounts, you can utilize the Migration Assistant, a built-in tool that transfers data between Macs.
To migrate user accounts using Migration Assistant, connect both Macs using a Thunderbolt cable or over a network. Launch Migration Assistant on the new Mac and follow the on-screen prompts.
Preferences
Preferences define how your Mac behaves, including display settings, keyboard shortcuts, and trackpad sensitivity. These settings are stored in various locations, including the Library folder and system preferences files.
To transfer preferences, ensure you have selected the “Preferences” option in Migration Assistant. This option copies relevant settings from the old Mac to the new one.
Network Configurations
Network configurations, such as Wi-Fi passwords, VPN settings, and network shares, are essential for connecting to the internet and accessing shared resources. Migration Assistant can transfer these configurations, simplifying the setup process on your new Mac.
During the migration process, ensure you have selected the “Network” option in Migration Assistant. This option copies your network settings, allowing you to connect to existing networks and access shared resources.
Printer Settings
Printer settings, including printer names, driver configurations, and print queues, are also transferred during a system migration. This ensures that you can continue using your printers without needing to reconfigure them.
Migration Assistant automatically copies printer settings, making the transition to your new Mac seamless.
Migrating your Mac system manually can be a bit of a pain, especially if you’re not sure what you’re doing. It’s kinda like trying to update your iPhone to iOS 14 without losing Fortnite – you need to be careful! If you’re worried about losing your precious game data, check out this guide: How to avoid losing Fortnite when updating to iOS 14.
Once you’ve got that figured out, you can tackle the Mac migration with a bit more confidence.
Keyboard Layouts
Keyboard layouts determine the language and character mappings used for typing. To ensure you can continue using your preferred keyboard layout, select the “Keyboard Layouts” option in Migration Assistant.
Migration Assistant automatically transfers your keyboard layout settings, preserving your typing preferences.
Troubleshooting
While migrating system settings is generally straightforward, issues can arise. If you encounter problems, ensure both Macs are connected properly and have sufficient storage space. If the migration fails, you can try restarting both Macs or running Migration Assistant again.
If you experience persistent issues, consult Apple’s support documentation or contact Apple Support for assistance.
Post-Migration Verification and Troubleshooting
After completing the migration process, it’s crucial to ensure that all your data, applications, and settings have been transferred successfully to your new Mac. You can also identify any potential issues that may have occurred during the migration and take steps to resolve them.
Verifying the Migration
Verifying the migration involves checking that all your data, applications, and settings are present and functioning correctly on your new Mac.
- Check your user data:Navigate to your user folder (usually found under Users/[your username]) and verify that all your documents, pictures, music, and other files are present. Open a few files to ensure they’re accessible and haven’t been corrupted.
- Launch applications:Open all the applications you frequently use and check if they are working correctly. This includes checking for any missing settings or preferences.
- Review system settings:Go to System Preferences and check your network settings, display settings, keyboard shortcuts, and other system-wide preferences to ensure they have been transferred correctly.
Common Post-Migration Issues
While macOS system migrations are generally reliable, there are a few common issues that can arise:
- Missing or corrupted data:This could be due to a problem during the migration process or a hardware issue with the source or destination Mac.
- Application compatibility issues:Some applications might not be compatible with the newer macOS version on your new Mac, resulting in crashes or errors.
- Incorrect settings:Some system settings might not have been transferred correctly, leading to unexpected behavior or functionality issues.
Troubleshooting Tips
If you encounter any issues during or after the migration, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Restart your Mac:A simple restart can often resolve minor issues and refresh the system.
- Check for updates:Ensure both your source and destination Macs have the latest macOS updates installed.
- Re-run the Migration Assistant:If you suspect data corruption, you can try running Migration Assistant again, selecting only the data that wasn’t transferred correctly.
- Contact Apple Support:If you’re unable to resolve the issue yourself, you can contact Apple Support for assistance. They can provide troubleshooting steps or offer remote assistance.
Security and Privacy
Moving your Mac’s data to a new system involves transferring sensitive information, making data security and privacy paramount. You need to take precautions to ensure your data is protected throughout the migration process and on the new system.
Data Security During Transfer
Protecting your data during transfer is crucial. Here are some recommendations:
- Use a Secure Connection:When transferring data over a network, use a secure connection like a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt the data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Encrypt External Drives:If using external drives for data transfer, encrypt them with a strong password to prevent data breaches if the drive is lost or stolen.
- Limit Data Exposure:Avoid transferring data over public Wi-Fi networks, which are often less secure.
Securing the New System
Once the migration is complete, it’s essential to secure your new system.
- Enable FileVault:FileVault encrypts your entire hard drive, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access your data.
- Install Anti-Malware Software:A reliable anti-malware program can protect your system from threats like viruses, malware, and spyware.
- Update Software Regularly:Keeping your operating system and applications up to date patches security vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Use Strong Passwords:Choose strong passwords that are difficult to guess and use a password manager to store them securely.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication:This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a code from your phone in addition to your password.
Ethical Considerations
Migrating sensitive data raises ethical considerations:
- Data Ownership and Privacy:You must respect the privacy of the data you are migrating, especially if it includes personal information.
- Data Security Practices:It’s important to ensure that the data you are migrating is being handled securely and ethically, in compliance with relevant data privacy laws and regulations.
- Transparency and Consent:Be transparent with users about how their data is being used and stored. Obtain their consent before migrating their data.
Alternative Migration Methods
While manually migrating your Mac system can provide a granular level of control, it can be a time-consuming and potentially complex process. Fortunately, several alternative migration methods offer more streamlined solutions. These methods leverage specialized tools to simplify the transfer of data, applications, and settings between Macs.
Apple’s Migration Assistant
Apple’s Migration Assistant is a built-in utility designed to simplify the migration process. It offers a user-friendly interface and handles most of the data transfer automatically. Migration Assistant provides several advantages:* Ease of use:The intuitive interface guides users through the migration process, making it accessible even for beginners.
Comprehensive transfer
It handles data, applications, and settings, ensuring a seamless transition.
Network and external drive compatibility
Migration Assistant supports both network and external drive transfers, offering flexibility in choosing the migration method.
Security and reliability
Migrating your Mac system manually can be a bit of a pain, especially if you’re not familiar with the process. But hey, at least you’re not trying to figure out how to activate your iPhone’s hidden pedometer, which can be a real head-scratcher.
How to activate the iPhone’s hidden pedometer Once you’ve got your Mac migration sorted, you can finally get back to focusing on the things that matter, like getting your daily steps in.
Apple’s built-in security features ensure data integrity and protection during the transfer.However, Migration Assistant also has some limitations:* Limited customization:It offers minimal customization options, potentially leaving some users with a less personalized experience.
Potential for data conflicts
If there are conflicts between existing data on the destination Mac and the transferred data, Migration Assistant may not handle them effectively.
Not suitable for all scenarios
Migration Assistant might not be the best choice for complex migrations involving specific applications or data types.
Third-Party Migration Tools
Third-party migration tools offer additional features and capabilities beyond what Apple’s Migration Assistant provides. These tools are developed by independent companies and cater to specific needs and preferences.Several advantages of using third-party migration tools include:* Advanced features:They often offer features like selective data migration, advanced filtering options, and data encryption for enhanced security.
Customization
These tools allow for greater customization, allowing users to tailor the migration process to their specific requirements.
Specialized capabilities
Some tools are designed for specific scenarios, such as migrating large amounts of data or transferring data between different operating systems.However, there are also potential drawbacks:* Compatibility issues:Ensure the tool is compatible with your Mac models and operating systems.
Cost
Some third-party tools may require a purchase, whereas others offer free versions with limited functionality.
Reliability
While reputable companies develop these tools, their reliability can vary, and it’s essential to research and choose a trustworthy option.
Choosing the Right Migration Method
The most appropriate migration method depends on individual needs and circumstances. Consider the following factors:* Data volume and complexity:For smaller, simpler migrations, Apple’s Migration Assistant might suffice. However, for large data volumes or complex migrations, third-party tools might offer more control and features.
Customization requirements
If you need a highly customized migration process, third-party tools provide greater flexibility.
Budget
Third-party tools may involve a cost, whereas Apple’s Migration Assistant is free.
Technical expertise
If you are comfortable with manual migration, you can opt for a more granular approach. However, if you prefer a simpler and more automated solution, Apple’s Migration Assistant or a third-party tool might be more suitable.
Tips for a Smooth Migration
Moving your entire Mac system to a new machine can be a daunting task, but with proper planning and preparation, you can make the process much smoother. Here are some tips to help you navigate the migration process successfully.
Planning and Preparation
It’s crucial to plan ahead to ensure a smooth migration.
- Back Up Your Data:Before you begin, create a full backup of your current Mac. This will serve as a safety net in case anything goes wrong during the migration process. Use Time Machine or other reliable backup solutions.
- Check Disk Space:Ensure you have enough free space on your destination drive to accommodate all your data, applications, and system files. You may need to free up space by deleting unnecessary files or transferring some data to external storage.
- Choose a Migration Method:Determine the best method for your needs. For a complete system migration, Apple’s Migration Assistant is usually the preferred option. If you only need to transfer specific files or folders, you can use external drives or cloud storage services.
- Review Your Applications:Identify applications that are no longer needed or compatible with your new Mac. Uninstall them before starting the migration to avoid unnecessary clutter.
- Prepare Your Destination Drive:Format the destination drive with the appropriate file system (usually APFS or macOS Extended). It’s best to start with a fresh, clean drive for optimal performance.
Managing Expectations
Understanding the process and managing expectations can help you avoid unnecessary stress during the migration.
- Set Realistic Timelines:Migration times can vary depending on the amount of data and the speed of your drives. Don’t expect it to be instantaneous. Be prepared to allocate several hours, especially for large systems.
- Expect Some Downtime:There will be some downtime while the migration is in progress. Plan accordingly and schedule it for a time when you can afford to be offline.
- Be Patient:The migration process can take time. Avoid interrupting the process or attempting to use your Mac during the migration.
Troubleshooting and Support, How To Perform a Manual Mac System Migration
Be prepared for potential issues and know where to turn for help if needed.
- Check for Error Messages:If you encounter any error messages during the migration, carefully read them and try to understand the problem. Consult Apple’s documentation or online support resources for solutions.
- Seek Professional Assistance:For complex or large-scale migrations, consider seeking professional assistance from a qualified technician or IT consultant. They can help ensure a smooth and successful transition.
Ultimate Conclusion
Migrating your Mac system manually can be a rewarding experience, giving you a deep understanding of your system and its components. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure a successful transition, minimizing downtime and maximizing data integrity.
Remember to take your time, back up your data regularly, and seek professional assistance if needed. Whether you’re a tech-savvy user or a beginner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the world of manual Mac system migrations.
FAQ Resource
Can I migrate to a newer macOS version using this method?
Yes, you can migrate to a newer macOS version using a manual migration. However, make sure the new macOS version is compatible with your Mac’s hardware. You can check Apple’s website for compatibility information.
What if I encounter issues during the migration process?
Don’t panic! There are resources available to help you troubleshoot common migration issues. Apple’s support website, community forums, and third-party resources can provide valuable guidance. If you’re still stuck, consider contacting Apple Support or a certified Mac technician.
Is it possible to migrate from a Time Machine backup instead of directly transferring data?
Yes, you can migrate from a Time Machine backup. This method is especially useful if you have a large amount of data and want to restore your system to a specific point in time. However, be aware that migrating from a Time Machine backup may not transfer all applications and settings.